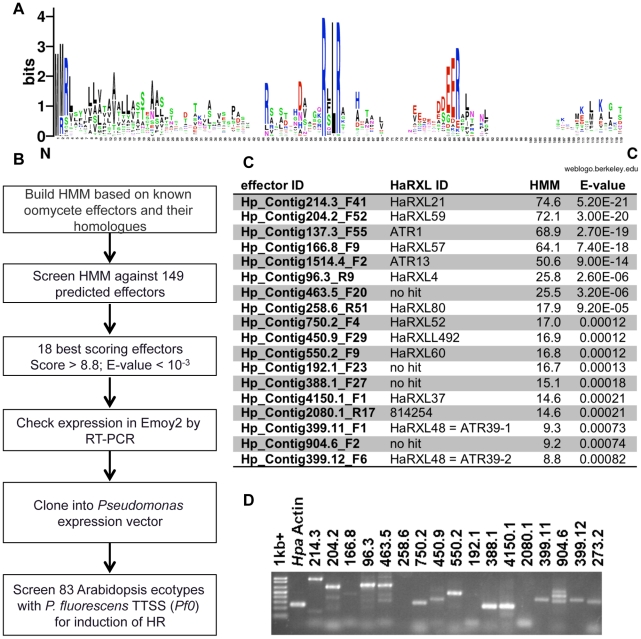
Figure 1. Identification of functional avirulence effector candidates from Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis (Hpa) using a Hidden Markov Model (HMM)–based search.
A) Consensus sequence of 43 oomycete effectors used in building the HMM. The consensus was generated using the Weblogo program. Larger letters signify higher conservation. B) Screening scheme for identification of effectors. The steps in the pipeline are as follows: 1) Building HMM model based on N-terminal secretion signal and RXLR domains of known effectors; 2) Screening the HMM against 149 predicted effectors to form a prioritized list; 3) Focusing on 18 best scoring effectors with HMM score >8.5 and E-value <0.001; 4) Determining expression of predicted effectors in Hpa Emoy2 7 days post-infection (dpi); 5) Cloning expressed effectors in Pseudomonas vector pPsSP [35] or pEDV3 [36] and determining expression in P. fluorescens; 6) Screening 83 Arabidopsis ecotypes with effectors for induction of resistance response, visible as HR. C) Summary of highest scoring effector candidates identified by HMM search. Effector IDs correspond to position on contigs in Hpa genome version 7.0. HaRXL IDs are the annotated IDs in the published Hpa genome version 8.3. “No hit” indicates genes not annotated in the final genome. HMM scores and E-values are indicated. D) Expression of effectors in Hpa Emoy2 infected tissue 7 dpi as determined by RT-PCR.