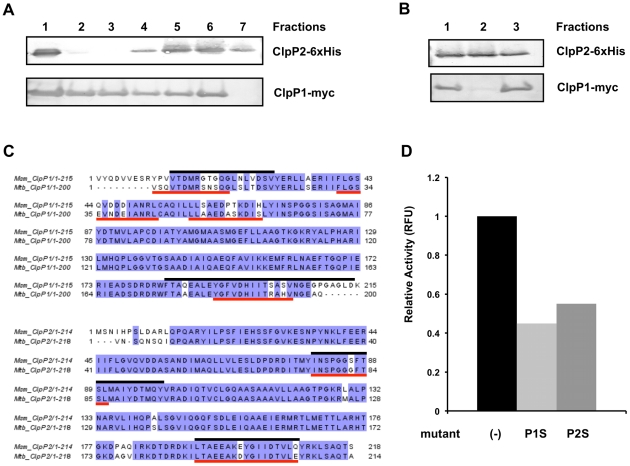
Figure 1. Mtb ClpP1 and ClpP2 interact, forming a multi-component protease, and share substantial similarity with ClpP1 and ClpP2 homologs in Msm.
(A) C-terminally myc-tagged Mtb ClpP1 and 6×His-tagged Mtb ClpP2 were expressed in Msm. Lysate (lane 1) was prepared and loaded onto a Ni-column. After washing with PBS (lanes 2,3), Ni-bound material was eluted with 50 mM (lane 4), 100 mM (lane 5), 250 mM (lane 6, 7) of imidazole in PBS, and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti α-myc and α-6×His antibodies. (B) Fraction 6 from (A) was applied to an anti-myc column (lane 1). The flow through (lane 2), and bound material (lane 3) were analyzed by immunoblot with α-myc and α-His antibodies. Bound material was released from the anti-myc agarose beads by boiling in Laemmli buffer after washing with PBS. (C) Bands representing ClpP1 and ClpP2 from (B) were sequenced by MS/MS revealing the presence of both Mtb and Msm homologs. Msm specific peptides are indicated by black lines, those specific to Mtb are indicated by red lines. (D) Cleavage of fluorescent peptide Z-Gly-Gly-Leu-AMC was measured in the presence of 1 µg ClpP1, 1 µg Clp2, and the activating peptide Z-Leu-Leu (see accompanying paper). Addition of 5 µg of catalytically inactive mutants of either ClpP1 (ClpP1S) or ClpP2 (ClpP2S) markedly inhibited cleavage by the ClpP1P2 protease. Results graphed are a representative sample of results obtained.