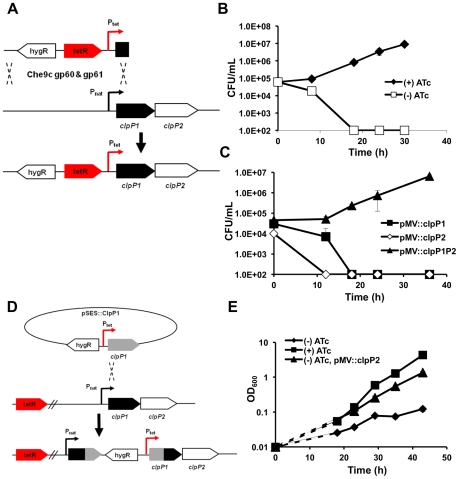
Figure 2. Both ClpP1 and ClpP2 are essential for normal growth in mycobacteria.
(A) Schematic representation of mycobacterial recombineering, employed to replace the endogenous promoter of the clpP1P2 operon with a ATc-inducible promoter (Msm strain ptet_clpP1P2). (B) Growth curves of Msm ptet_clpP1P2 in the presence (50 ng/mL) or absence of inducer ATc. Data are represented as mean CFU/mL +/− standard deviation. (C) Growth curves of Msm ptet_clpP1P2 complemented with clpP1, clpP2 or both clpP1 and clpP2 in the absence of inducer ATc. Data are represented as mean CFU/mL +/− standard deviation. (D) Schematic representation of genetic strategy used to create a tetracycline inducible conditional Msm ClpP2 mutant (Msm strain ptet_ClpP2) (E) Growth curves of Msm ptet_clpP2 in the presence (50 ng/mL) or absence of inducer ATc. Msm ptet_clpP2 was also complemented with clpP2 in the absence of ATc. Data are represented as mean OD600 +/− standard deviation. Dashed lines represent assumed growth rates until first measured growth point.