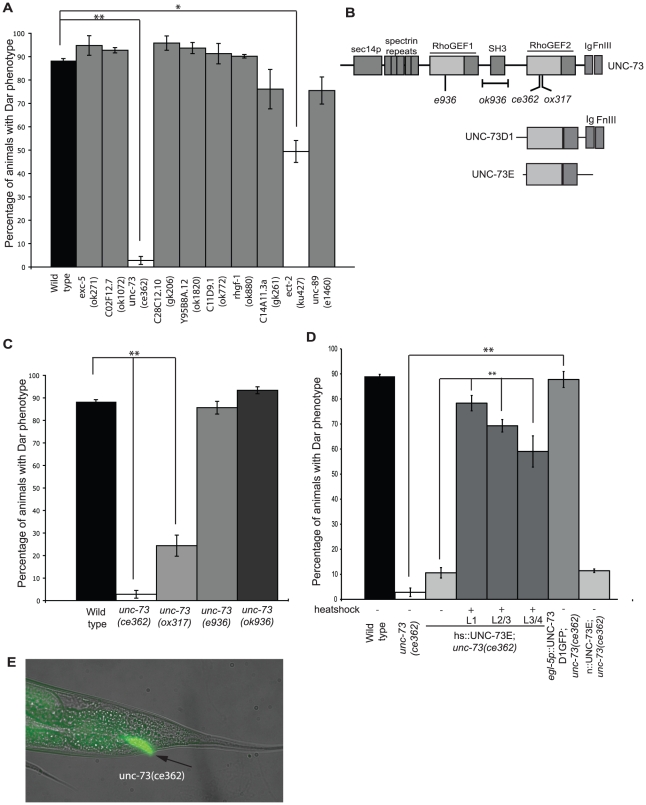
Figure 2. UNC-73 (Trio) is required in rectal epithelial cells for the Dar response to infection.
Viable RhoGEF mutants were infected with M. nematophilum and the percentage of Dar animals scored. Mutations in unc-73(ce362), and ect-2(ku427), but not other RhoGEF's, significantly decreased the percentage of Dar animals (A). The UNC-73 gene contains two RhoGEF domains, one specific for Rac (RhoGEF1) and the other specific for Rho (RhoGEF2) (B). Animals with mutations that prevented Rac activation (unc-73(e936) and (ok936)) had a wild-type Dar response whereas mutations in RhoGEF2 (unc-73(ce362) and (ox317)) significantly decreased the percentage of Dar animals (C). Expression of UNC-73 isoforms E or D1 using heat shock at L1, L2/L3 and L3/L4 stage (hs::UNC-73E) or rectal epithelial (egl-5p::UNC-73D1::GFP), but not neuronal (n::UNC-73E), expression rescued the Dar phenotype in unc-73(ce362) animals (D). Although unc-73(ce362) animals failed to produce a Dar response M. nematophilum bacteria, labeled using the nucleic acid stain SYTO13, still attached to the anal opening (E), the rectal opening is indicated with an arrow).