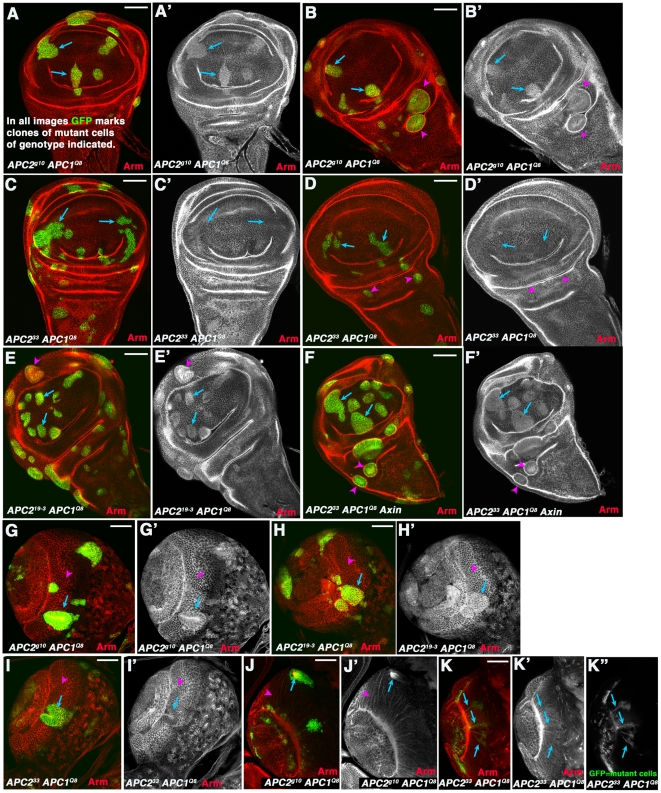
Figure 7. APC233 has a hypomorphic phenotype.
A–F. 3rd instar wing imaginal discs. G–K. 3rd instar larval brains. Clones of mutant cells of the indicated genotype were induced using the MARCM method [42] and homozygous mutant cells are marked by the presence of GFP. A–B. Cells in the wing pouch that are APC2g10 APC1Q8 double mutant accumulate modestly elevated levels of Arm (arrows), while mutant cells in regions surrounding the wing pouch segregate and form cysts (arrowheads). C,D. In contrast, cells in the wing pouch that are APC233 APC1Q8 double mutant do not accumulate elevated levels of Arm (arrows), and mutant cells in regions surrounding the wing pouch do not always segregate to form cysts (arrowheads). E,F. Clones of cells that are APC219-3 APC1Q8 double mutant (E) or APC233 APC1Q8 Axin triple mutant (F) behave like APC2g10 APC1Q8 double mutant cells. G. Neurepithelial cells in anterior medullar region of the larval brain that are APC2g10 APC1Q8 double mutant accumulate modestly elevated levels of Arm (arrow) and segregate from neighbors, in contrast to neighboring wild-type cells (arrowhead; [18]). H. Neurepithelial cells in anterior medullar region of the larval brain that are APC219-3 APC1Q8 double mutant behave similarly to APC2g10 APC1Q8. I. Neurepithelial cells in anterior medullar region of the larval brain that are APC233 APC1Q8 double mutant sometimes segregate but do not always accumulate elevated Arm levels (arrow vs. arrowhead). J. Medullar neurons that are APC2g10 APC1Q8 double mutant invariably send out axons into the center of the clone, forming axonal knots (arrow; [18]) instead of the normal finely fasciculated projections (arrowhead) to the medullar neuropil [18]. K. Some medullar neurons that are APC233 APC1Q8 double mutant do not form axonal knots but instead send normal projections to the medullar neuropil (arrows). Scale bars = 50 µm.