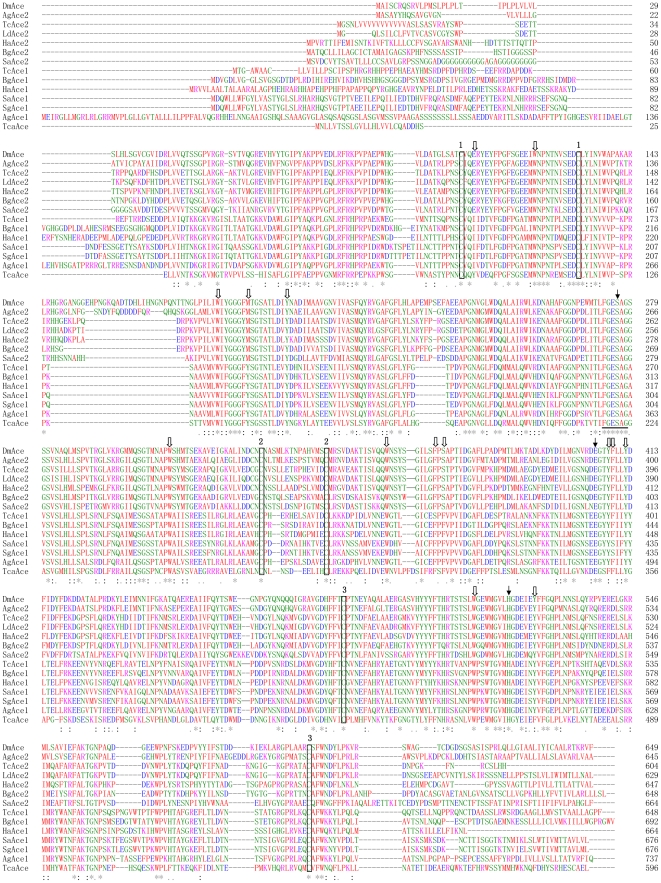
Figure 2. Alignment of deduced AChE protein sequences encoded by TcaAce (CAA27169, Torpedo californica Ace); TcAce1 (HQ260968, Tribolium castaneum Ace1, this paper); TcAce2 (HQ260969, T. castaneum Ace2, this paper); SaAce1 (AY819704, Sitobion avenae Ace1); SaAce2 (AY707319, S. avenae Ace2); DmAce (X05893, Drosophila melanogaster Ace); AgAce1 (XM_321792, Anopheles gambiae Ace1); AgAce2 (BN000067, A. gambiae Ace2); BgAce1 (DQ288249, Blattella germanica Ace1); BgAce2 (DQ288847, B. germanica Ace2); HaAce1 (DQ001323, Helicoverpa assulta Ace1); HaAce2 (AY817736, H. assulta Ace2); SgAce1 (AF321574, Schizaphis graminum Ace1) and LdAce2 (L41180, Leptinotarsa decemlineata Ace2).
Numbering of the amino acid sequences was from the N-terminus of mature proteins. Identical amino acids were indicated by asterisks and conservative substitutions by dots. The catalytic triad residues were marked with arrowhead. The number 1, 2, 3 on the boxed amino acids indicated the residues forming intramolecular disulfide bonds. The positions of aromatic residues lining the active site gorge in T. californica AChE were marked with block arrows. The cholinesterase signature sequence was underlined.