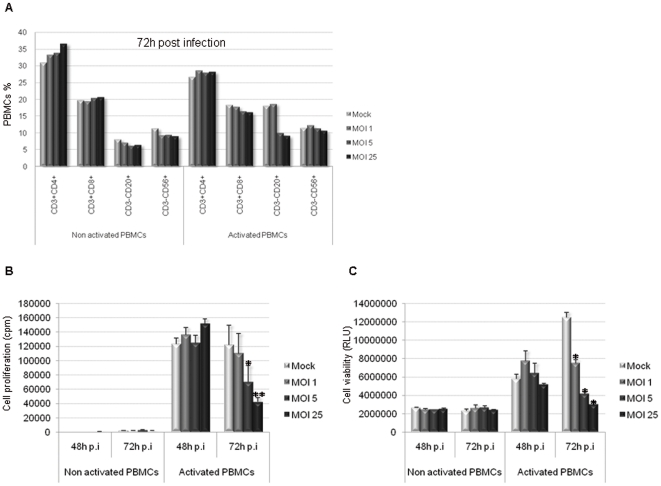
Figure 1. PHA-activated PBMCs are affected by H-1 PV infection.
PBMCs were inoculated with increasing amounts of purified H-1 PV or mock-treated. MOI : multiplicity of infection, expressed as the number of plate-forming unit/cell; p.i : post-infection. A. CD8+ effector T cell, B lymphocyte and NK cell populations are affected by H-1 PV infection within PHA-activated PBMCs, whereas CD4+ helper T cells are not. Cells were collected 72 h p.i and labelled for appropriate cell surface antigens and the fraction of main lymphocyte populations within PBMCs was analyzed using flow cytometry. Results are expressed as percentages of total cells within PBMCs. B. PHA-activated PBMC proliferation ability is decreased upon H-1 PV infection. Cell proliferation was assessed by metabolic incorporation of tritiated thymidine into cellular DNA. Assays were performed at different times after H-1 PV inoculation but only 48 and 72 h p.i conditions are shown. Results from one representative experiment are represented as means of triplicate wells with ± standard deviation bars and expressed in count per minute (cpm). Statistical analysis for 4 independent experiments was performed using a Mann-Whitney test (* p<0,05; ** p<0,01 relative to Mock condition). C. PBMCs viability is decreased upon H-1 PV infection. Cell viability was evaluated using a test based on a bioluminescent reaction measuring the amount of ATP present in living cells. Assays were performed at different times after H-1 PV inoculation but only 48 and 72 h conditions are shown. Results from one representative experiment are represented as means of trilplicate wells with ± standard deviation bars and expressed in relative light unit (RLU). Statistical analysis for 4 independent experiments was performed using a Mann-Whitney test (* p<0,05 relative to Mock condition). Representative data from 4 independent experiments.