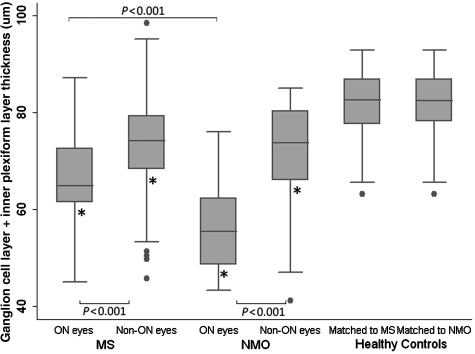
Figure 4.
Cross sectional analysis of multiple sclerosis (MS) and neuromyelitis optica (NMO) participants with and without a history of optic neuritis and healthy controls. The ganglion cell layer (GCL) plus inner plexiform layer (IPL) thickness of optic neuritis (ON) and non-optic neuritis (non-ON) eyes of participants with multiple sclerosis and with neuromyelitis optica were reduced when compared with controls (P < 0.001 for all comparisons-indicated by an asterisk). Optic neuritis eyes of both multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica eyes were significantly reduced when compared with non-optic neuritis eyes and optic neuritis eyes of patients with neuromyelitis optica were reduced when compared with optic neuritis eyes of participants with multiple sclerosis (P < 0.001). The error bars represent the 5th and 95th percentiles of the measure.