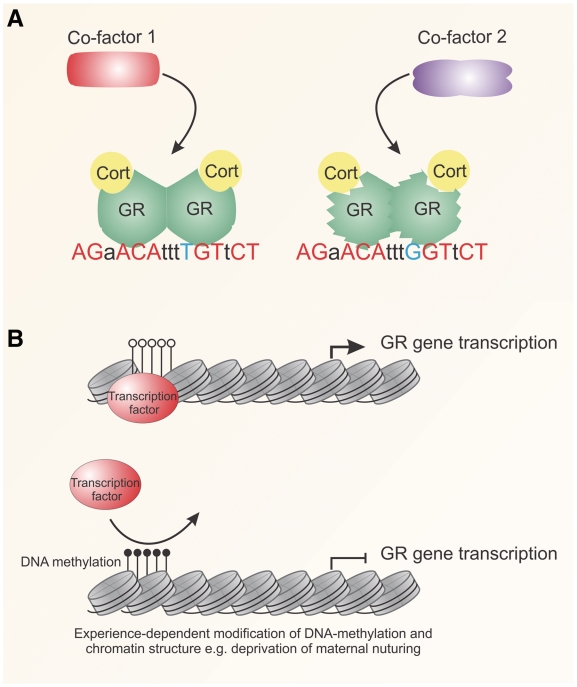
Fig. 3.
Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms in GR action. (A) DNA is an allosteric modulator, altering the structure of the receptor when bound to DNA. SNPs (blue) at GREs (red) could alter the interactions with co-factors by influencing GR structure. The effects might contribute to gene- and individual-specific gene regulation. (B) DNA methylation, an epigenetic mechanism, acts to silence gene transcription by altering chromatin structure. Individual-specific experiences, such as maternal nurturing, can alter DNA methylation patterns, producing expression patterns heritable across generations. The reduction in GR expression causes resistance to hormone action in specific tissues. Cort: cortisol.