Figure 4.
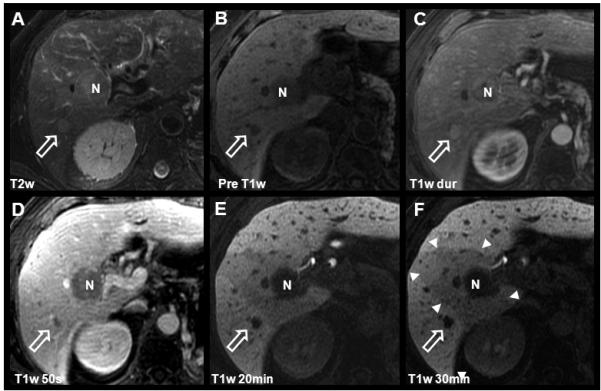
Detection and characterization of HCC using gadoxetic acid. Images from this 68 year-old male with known multifocal HCC include findings after chemotherapy and TACE procedure. Two hypointense lesions are seen on pre-contrast and delayed T1w images (B, E, F): The white open arrow indicates the untreated HCC with characteristic T2w hyperintensity, intense arterial enhancement, and rapid portal venous phase washout. N indicates a necrotic area after radiofrequency ablation (RFA). Note the wedge-shaped perfusion deficit (white arrowheads) associated with a thrombosis of the right portal vein (not shown). Also note the contrast in the biliary tract, on 20 minute post-contrast images (E) using gadoxetic acid as compared to figs. 1 and 3.
