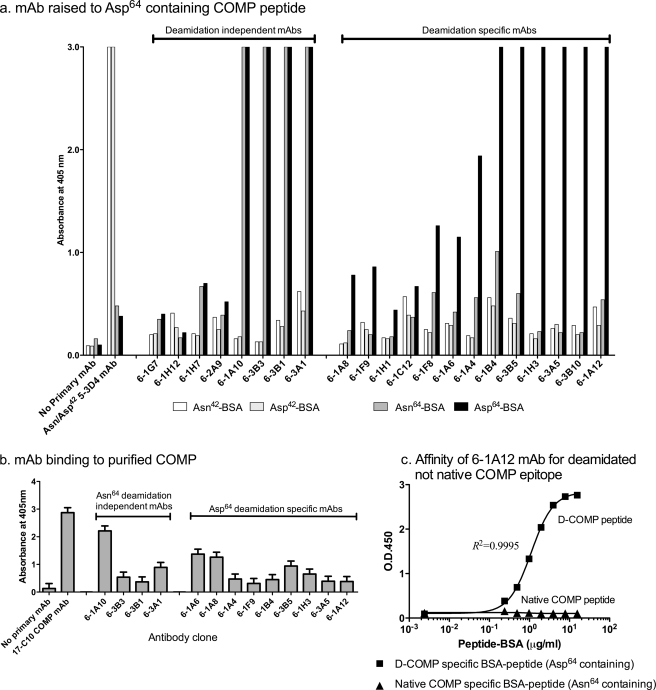
FIGURE 1.
Monoclonal antibody specificity of mAbs raised to the COMP-deamidated epitope Asp64. a, screening of mAbs against deamidated and native COMP peptides. Two native COMP BSA-peptide constructs, Asn42 (BSA-CELQETN42AALQ) and Asn64 (TFLKN64TVMEC-BSA), and the corresponding two deamidated BSA constructs, Asp42 (BSA-CELQETD42AALQ) and Asp64 (TFLKD64TVMEC-BSA), were coated onto 96-well plates. Hybridoma culture media were incubated with the coated plates for 2 h before addition of goat anti-mouse alkaline phosphatase secondary antibody and ELISA development using OPD substrate. A negative control containing no primary antibody was included, and a mAb raised against CELQETD42AALQ was used to confirm immunoreactivity of the BSA-CELQET(N/D)42AALQ control peptides. Screening yielded a total of eight deamidation-independent (immunoreactivity to Asn64 and Asp64) and 13 deamidation-dependent mAbs (preferential immunoreactivity to Asp64). b, screening of mAbs against purified cartilage COMP. Purified COMP protein (a generous gift from V. Vilim) was coated onto 96-well plates. Hybridoma culture media were incubated with the coated plates for 2 h before addition of goat anti-mouse alkaline phosphatase secondary antibody and ELISA development using OPD substrate. A negative control containing no primary antibody and a positive control using the anti-COMP 17-C10 mAb were included. c, mAb 6-1A12 preferentially reacted against deamidated COMP peptide and not the native COMP sequence. To test the affinity of the 6-1A12 mAb for both native and deamidated COMP, different concentrations of either the D-COMP Asp64 specific TFLKD64TVMEC-BSA or the native COMP-specific Asn64 TFLKN64TVMEC-BSA were coated onto a 96-well plate in a direct ELISA, performed as for a. A standard curve with an appropriate dose response is generated for 6-1A12 and the deamidated COMP Asp64-BSA construct; 6-1A12 did not recognize the native Asn64-BSA construct.