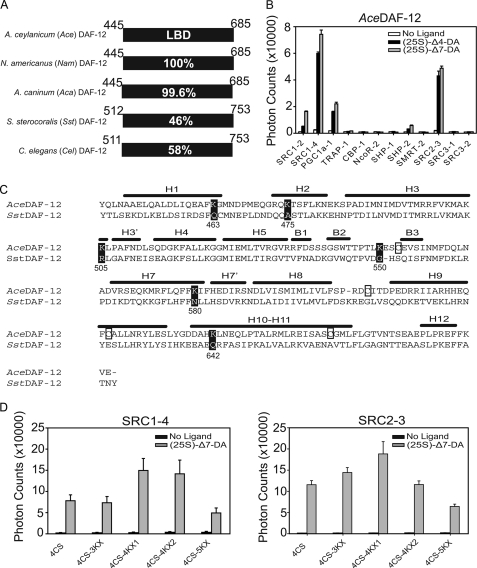
FIGURE 1.
Strategy for crystallization of the AceDAF-12 LBD. A, sequence identity of DAF-12 homologs from parasitic nematodes. Numbers refer to the amino acid position in the LBD of each receptor. Amino acid 449 is alanine in AceDAF-12 and NamDAF-12 but is valine in AcaDAF-12. B, AlphaScreen assays to search for AceDAF-12-interacting peptides. 1 μm (25S)-DA is used. C, alignment of secondary structural elements of the AceDAF-12 LBD is based on the crystal structure of the SstDAF-12 LBD. H, α-helix; B, β-strand. Cysteines in AceDAF-12 that were mutated to serines are boxed. Lysines in AceDAF-12 that were mutated to the corresponding amino acids in SstDAF-12 are highlighted in black. Numbers refer to the lysine position in the AceDAF-12 LBD. D, ligand binding function of AceDAF-12 mutants for crystallization is examined in AlphaScreen assays. 4CS, C553S/C607S/C625S/C661S; 4CS-3KX, K475A/K505R/K550G plus 4CS; 4CS-4KX1, K475A/K505R/K550G/K642Q plus 4CS; 4CS-4KX2, K463Q/K475A/K505R/K550G plus 4CS; 4CS-5KX, K475A/K505R/K550G/K580N/K642Q plus 4CS. 1 μm (25S)-DA is used. 4CS-4KX1 was successful for subsequent crystallization.