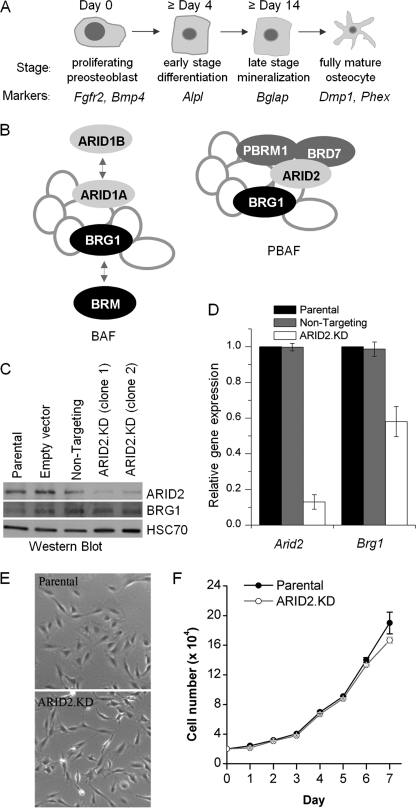
FIGURE 1.
Generation of stable ARID2-depleted MC3T3-E1 cell lines. A, the program of osteoblast differentiation can be divided into four phases: (a) proliferative pre-osteoblasts expressing Fgfr2 and Bmp4; (b) early differentiation characterized by Alpl expression; (c) late differentiation distinguished by highly induced expression of Bglap (encoding osteocalcin); and (d) terminal differentiation to the fully mature osteocyte phenotype marked by expression of Dmp1 and Phex. B, the multisubunit SWI/SNF complex contains a core ATPase plus seven or more non-catalytic subunits. The BAF complex can contain either the BRG1 or the BRM ATPase; its signature subunits are the mutually exclusive ARID1A and ARID1B proteins. The PBAF complex is only known to contain BGR1; it is distinguished by the presence of three unique subunits: ARID2 (alias BAF200), polybromo/PBRM1 (alias BAF180), and BRD7. C, total cell lysates from parental cells, cells transfected with an empty vector, vectors encoding a non-targeting control sequence, or either of two lines expressing ARID2-targeting sequences (ARID2.KD) were probed in a Western blot with antibodies specific to either ARID2 or BRG1. The constitutively expressed HSC70 protein was used as a loading control. D, expression of Arid2 and Brg1 in ARID2-depleted cells (ARID2.KD, clone 1) or the cell line transfected with the non-targeting control sequence, relative to the parental cells, was determined by qRT-PCR, normalized to Gapdh expression. Shown are mean values relative to the parental line with the S.E. (n = 3). E, representative pictures of the general morphology of parental cells and ARID2-depleted cells. F, the growth rate of parental and ARID2.KD cells. Cells were seeded in 6-well plates at 2 × 104 cells/well, and the medium was changed on day 4 after seeding. Each point on the growth curve shows the mean value with the S.E. from three wells.