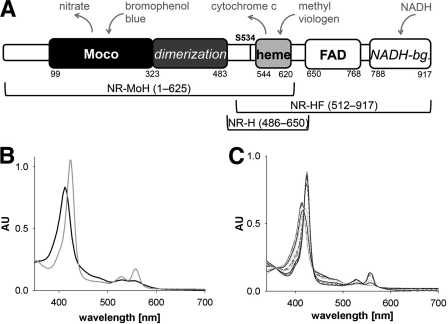
FIGURE 1.
Domain structure and spectral properties of NR and NR fragments. A, domain structure of NR. Numbers indicate first/last residues of a domain, and cofactors are written in bold. The dimerization domain and NADH-binding (NADH-bg.) lobe are italicized, and the regulatory crucial serine residue Ser-534 is labeled (as S534). Above, electron donors and acceptors are shown in gray. Below, NR fragments and their respective lengths are depicted (NR-MoH, Mo-heme fragment; NR-HF, heme-FAD fragment; NR-H, heme fragment). B and C, UV-visible spectra of Mo-heme (6.9 μm) following the reduction with dithionite (gray trace) and reoxidation with nitrate (black trace) (B) and oxidized heme-FAD fragment (5.4 μm) (black trace) (C) in the course of titration with a stock solution of 200 μm NADH (gray traces). AU, absorbance units.