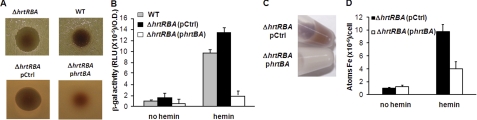
FIGURE 5.
The HrtBA transporter controls environmental heme toxicity through efflux in L. lactis. A, HrtBA controls heme toxicity. Stationary phase cultures of WT, ΔhrtRBA, and ΔhrtRBA strains carrying either a control plasmid (pG+host8, designated pCtrl) or phrtBA were plated on solid medium. Hemin (10 μl of a 10 mm stock solution) was pipetted directly onto plates, which were incubated at 30 °C for 24 h. Inhibition zones appear as dark clearing in the center of each panel. Results are representative of at least three experiments. B, HrtBA regulates intracellular heme content. β-Gal activity of the pPhrthrtR-lac plasmid, established in WT, ΔhrtRBA(pCtrl), or ΔhrtRBA(phrtBA) strains, was evaluated on bacteria cultivated without or with 5 μm hemin. β-Gal activity was quantified by luminescence. Results represent the mean ± S.D. from triplicate experiments. C, color phenotype of ΔhrtRBA transformed with pCtrl and ΔhrtRBA carrying phrtBA. Bacteria were grown to A600 = 0.5 prior to addition or not of 10 μm hemin in the culture medium for an additional hour. Bacteria were pelleted by centrifugation. Control bacteria exhibited a strong red color, whereas bacteria overexpressing HrtBA did not. D, iron ([57Fe] content determination of ΔhrtRBA(pCtrl) and ΔhrtRBA(phrtBA) strains grown as in C in the absence and presence of 57Fe-hemin. Results represent the mean ± S.D. from triplicate experiments.