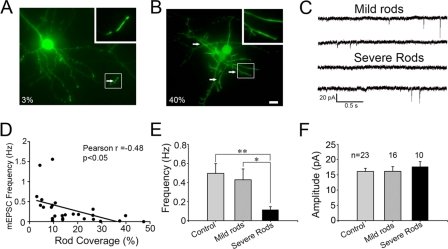
FIGURE 6.
Effect of cofilin rods on mEPSCs. A and B, examples of cofilin-transfected neurons with mild rods (A, 3% rod coverage) and severe rods (B, 40% rod coverage). Arrows point to typical rods. Scale bar, 10 μm. C, representative traces of mEPSCs recorded in neurons with mild or severe rods. D, Pearson's correlation test revealing the inverse correlation between rod coverage and mEPSC frequency (n = 26, r = −0.48, p < 0.05). E and F, bar graphs showing that severe rods resulted in a significant decrease of mEPSC frequency (E), but not amplitude (F). Neurons were transfected at 6–9 days in vitro and recorded at 10–12 days in vitro. mEPSC frequency: control 0.5 ± 0.1 Hz (n = 23), mild rods 0.43 ± 0.11 Hz (n = 16), severe rods 0.12 ± 0.03 Hz (n = 10); mEPSC amplitude: control 16.1 ± 1.0 pA, mild rods 16.1 ± 1.6 pA, severe rods 17.7 ± 1.7 pA. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.