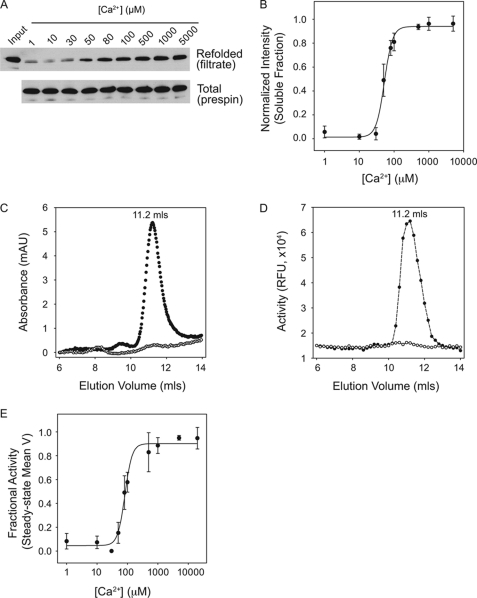
FIGURE 2.
Calcium-induced AP folding. Full-length alkaline protease was purified for binding and activation studies to evaluate the role of Ca2+ binding on AP folding. A, AP refolding was assessed after rapid dilution into Ca2+-containing buffers and filtration through a Microcon YM-100 filter. A representative Western blot of the filtrate (top) and total protein (bottom) is shown for Ca2+ concentrations between 1 μm and 5 mm. B, the refolded fraction of AP after filtration was assessed by densitometry and is shown as a function of Ca2+ in the refolding buffer. C, analytical gel filtration chromatography was used to evaluate the hydrodynamic radius of purified AP. Protein was refolded in the absence of Ca2+ (open circles) or in 20 mm Ca2+ (filled circles) and filtered prior to column injection. D, protease activity was assessed from fractions collected after gel filtration. Proteins refolded in the absence of Ca2+ (open circles) and in 20 mm Ca2+ (filled circles) were evaluated utilizing the BODIPY-casein substrate. E, mean velocities of the steady-state activities of AP refolded are shown plotted against Ca2+. Non-linear, least squares regression fit to a four-parameter Hill equation is shown as a solid line in B and E. Data are shown as mean ± S.D. (error bars).