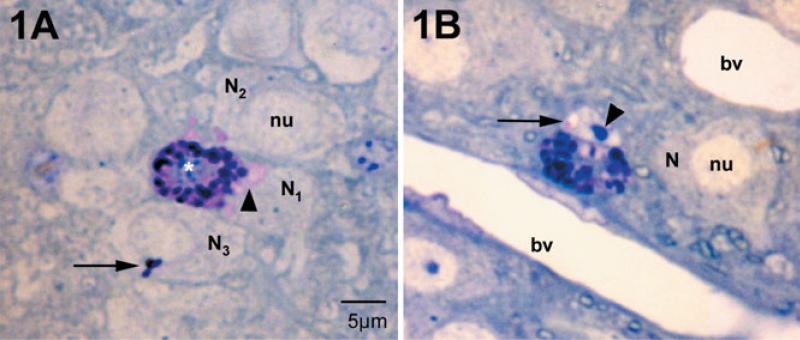
Fig. 1.
Mast cells and neurons in the medial habenula as visualized in 1-μm plastic sections stained with toluidine blue, pH 11. Mast cells are distinguished from neurons by their large secretory granules and heterochromatic nucleus (white asterisk). Nuclei (nu) of neighboring neurons (N) are euchromatic. (A) The mast cell cytoplasm is filled with intensely stained granules. Those that are intact are blue to purple. Small regions of the cytoplasm are pink and are sites of granules undergoing degranulation. In the neighboring neurons, N1 and N2, patches of pink are present in the cytoplasm (arrowhead). In N3 a small cluster of stained granules is present (arrow). N1 and N2 correspond to the electron micrograph in Fig. 3. (B) In this instance the neuronal nucleus contains pink material apparently in a small sac (arrow); this cell is cut through the nucleolus (arrowhead). This cell is also shown in the electron micrograph in Fig. 4. bv, blood vessel.