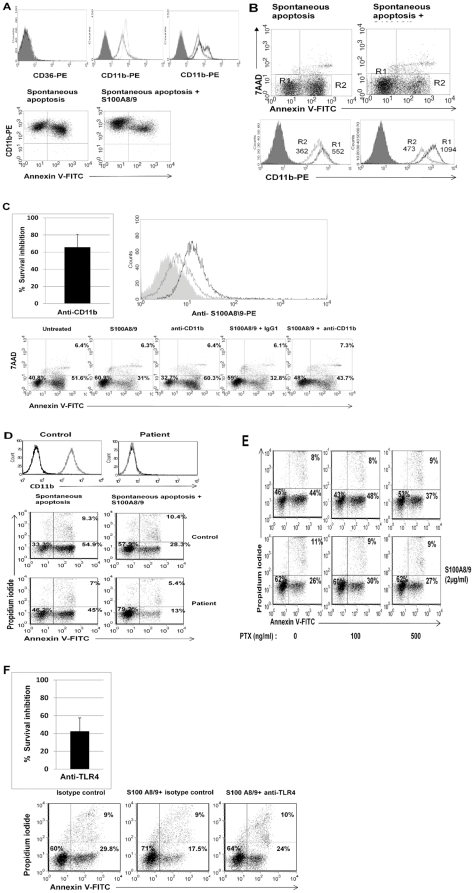
Figure 5. The survival effect of S100A8/9 is mediated through CD11b/CD18 and TLR4.
A. Expression of CD11b on neutrophils. Upper panel. Freshly isolated neutrophils express CD11b/CD18 (isotype control is shown as filled histogram and anti- CD11b/CD18-PE in dotted line, middle) but not CD36 (left). Following 12 h of spontaneous PCD (gray line, middle) there was a marked decrease in the expression of CD11b/CD18 in comparison to freshly isolated neutrophils. Addition of S100A8/9 resulted in two different cell populations: high and low-CD11b/CD18 (black line, right). Lower panel. Left. Correlation between CD11b and phosphatidylserine expression demonstrates that when neutrophils become apoptotic they downregulate CD11b expression. Right. S100A8/9 upregulates CD11b expression. B. S100A8/9 dramatically increases CD11b on viable cells. Viable cells (R1, black line) increase CD11b expression from a mean fluorescence of 552 to 1094 (p<0.0001). Apoptotic cells (R2, gray line) still maintain some of this effect and show a mean fluorescence of 473, compared to 362 in the absence of S100A8/9. Filled histograms represent isotype control. Neutrophils were harvested after 12 h spontaneous constitutive PCD, with or without treatment with 2 µg/ml S100A8/9. Histograms are representative of at least 3 different experiments. C. The survival effect of S100A8/9 in the presence of anti-CD11b/CD18. Upper panel. Right. Neutrophils were incubated for 12 h and treated with either anti-CD11b or the isotype control IgG1 before addition of S100A8/9 complex. Integrin inhibition reduced the effect of S100A8/9 by 40−100% in comparison with the isotype control (p<0.001). The average of 6 experiments is presented. Lower panel. A representative dot plot is shown. Upper panel. Left. S100A8/9 binds to CD11b/CD18. CHO cells transfected with CR3 (black) or vector (gray) were evaluated for S100A8/9 binding. CR3-ransfected cells bound at rates almost twofold higher than CHO control cells (median fluorescence 13.3 vs. 6.6, p<0.001). The filled curve represents isotype control; the histogram is representative of 3 experiments. D. S100A8/9 effect on neutrophils from a CD11b/CD18-deficient patient. Neutrophil expression of CD11b from a healthy control and a patient with leukocyte adhesion deficiency is shown in the upper panel. Spontaneous constitutive apoptosis is shown in the lower panel, together with the S100A8/9 effect. Neutrophils were isolated from a CD11b-deficient patient and a healthy control, as described in Materials and methods, incubated at a concentration of 1×106/ml and allowed to undergo spontaneous constitutive PCD for 10 h, with or without addition of S100A8/9. Apoptosis was assessed by Annexin V-PI staining. E. The survival effect induced by the complex S100A8/9 in the presence of pertussis toxin. Bordetella pertussis toxin at 100 and 500 ng/ml were added to neutrophils 45 min before adding S100A8/9. Neutrophils then were allowed to undergo constitutive spontaneous PCD that was assessed using AnnexinV-FITC and PI staining after 12 h. The dot plots are representative of 3 experiments. F. The survival effect of S100A8/9 in the presence of anti-TLR4. Neutrophils were incubated for 10 h and treated with either anti-TLR4 or the isotype control IgG2a, as described in Materials and methods. Inhibition of TLR4 abrogated the effect of S100A8/9 by 30−60% (p<0.001) in comparison with the isotype control, as seen in upper panel. The upper panel is presented as percentage of control. The experiment is a summary of four experiments (upper panel) with representative Plots in the lower panel.