Table 3. Genotype counts and their transmissions used by 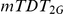 .
.
| Nontransmitted | Nontransmitted | ||||||||||||
| haplotype | haplotype | ||||||||||||
| Transmitted |
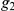
|
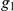
|
Transmitted |
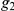
|

|
||||||||
| haplotype | AB | Ab | aB | ab | Total | haplotype | AB | Ab | aB | ab | Total | ||
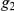
|
AB |

|
30 | 3 | 7 | 40 |

|
AB |
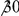
|
24 | 5 | 5 | 34 |

|
Ab | 37 |
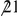
|
6 | 5 | 48 |
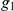
|
Ab | 31 |
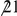
|
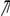
|
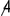
|
31 |
| aB | 8 | 6 |
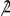
|
3 | 17 | aB | 9 |
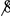
|
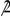
|
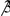
|
9 | ||
| ab | 11 | 3 | 1 |
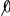
|
15 | ab | 11 |
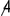
|
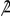
|
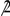
|
11 | ||
| Total | 56 | 39 | 10 | 15 | 121 | Total | 51 | 24 | 5 | 5 | 85 | ||
Haplotypes in rows represent those transmitted haplotypes at each genotype. Haplotypes in columns represent those nontransmitted haplotypes at each genotype. Homozygous genotype counts (diagonal) are crossed off the tables as they are not used to compute 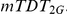 Left grid: genotype counts from the training data set (see Table 2) used to make up groups
Left grid: genotype counts from the training data set (see Table 2) used to make up groups  and
and  in
in 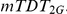 Groups are:
Groups are: 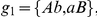 with those haplotypes with
with those haplotypes with 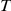 counts larger than
counts larger than 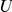 counts (Ab:
counts (Ab: 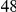 versus
versus 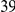 and aB:
and aB: 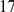 versus
versus 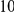 ) and
) and 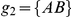 with
with 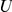 counts larger than
counts larger than 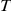 counts (
counts (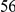 versus
versus 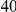 ). Right grid: genotype counts from the test data set used to compute the statistic. As the length similarity measure is used to assign an haplotype to a group, and the two most similar haplotypes to haplotype
). Right grid: genotype counts from the test data set used to compute the statistic. As the length similarity measure is used to assign an haplotype to a group, and the two most similar haplotypes to haplotype 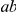 belongs to group
belongs to group 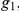
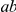 is assigned to
is assigned to  All the haplotypes belonging to the same group are considered of having an equivalent effect and are collapsed. Therefore, parental genotypes in the test data set with haplotypes belonging to the same group are considered as homozygous and not used by
All the haplotypes belonging to the same group are considered of having an equivalent effect and are collapsed. Therefore, parental genotypes in the test data set with haplotypes belonging to the same group are considered as homozygous and not used by 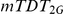 (they are crossed off the table too).
(they are crossed off the table too).
