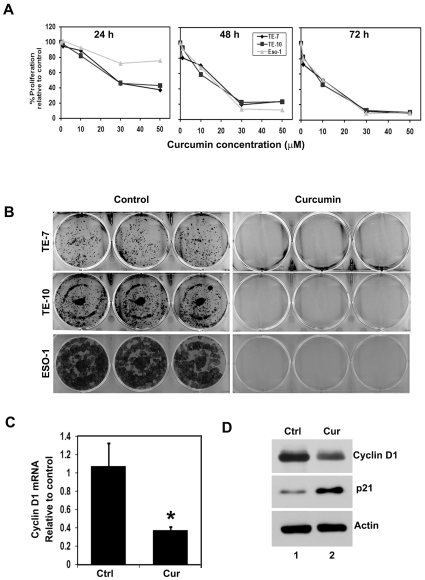
Figure 1. Curcumin inhibits esophageal cancer cell proliferation.
(A) Curcumin inhibits proliferation of esophageal cancer cells. Cells were incubated with increasing doses of curcumin (0–50 µM) for up to 72 h and analyzed for cell proliferation. Curcumin treatment resulted in a significant dose- and time-dependent decrease in cell proliferation in all three cells when compared with untreated controls. (B) Curcumin inhibits colony formation. Esophageal cancer cells were incubated with 30 µM of curcumin for 24 h and allowed to grow into colonies for 10 days. Incubation with curcumin inhibits colony formation. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Cyclin D1 is one the cell cycle regulatory protein and which is involved in the cell cycle arrest. RNA from TE-7 incubated with 30 µM curcumin was subjected to Real Time PCR for cyclin D1 mRNA expression. Curcumin treatment significantly inhibits cyclin D1 mRNA expression (*p<0.05). (D) Lysates from TE-7 incubated with 30 µM curcumin were analyzed by western blotting for cyclin D1 expression levels using mouse anti-cyclin D1 antibody. Curcumin treatment inhibits cyclin D1 protein expression.