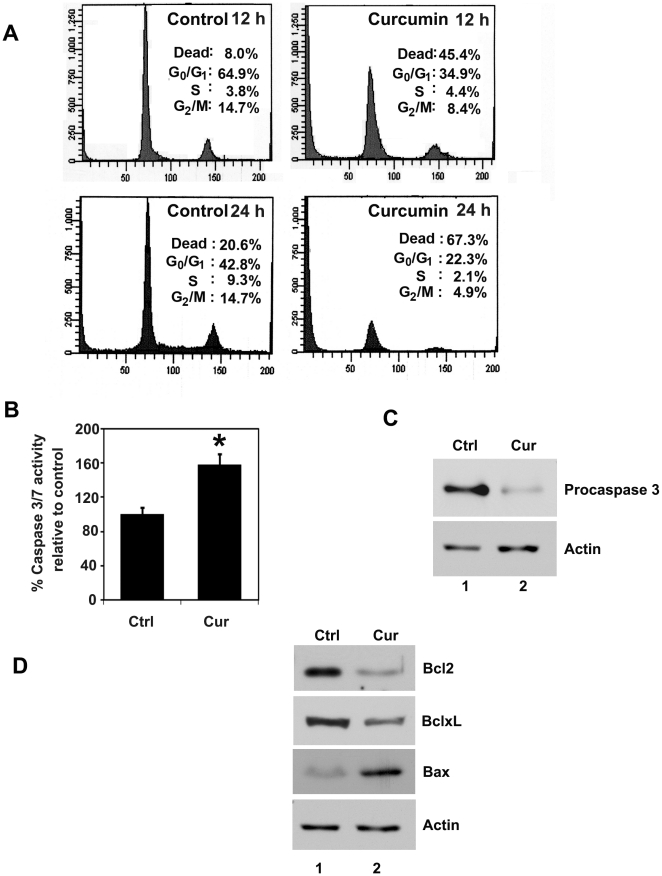
Figure 2. Curcumin induces cell death and apoptosis.
(A) Cell cycle analysis of curcumin treated cells. TE-7 cells were treated with 30 µM of curcumin for 12 and 24 h, examined by flow cytometry following propidium iodide staining for DNA content. Curcumin treatment leads to increased number of dead cells. Graphs are representative of data collected from three experiments. (B) Curcumin induces caspase-3, an apoptosis mediator. TE-7 cells incubated with 30 µM of curcumin were analyzed for apoptosis by caspase-3 and-7 activation. Curcumin treatment increased the number of cells undergoing apoptosis compared to untreated controls (*p<0.05). (C) Lysates from TE-7 cells incubated with 30 µM of curcumin were analyzed by western blotting for caspase-3 protein levels using rabbit anti-caspase-3 antibody. Curcumin treatment resulted in decreased procaspase-3. (D) Lysates from TE-7 cells incubated with 30 µM of curcumin were analyzed by western blotting for Bcl2, BclxL, and Bax proteins. Curcumin reduces expression of anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl2 and BclxL, whereas increased expression of pro-apoptotic proteins in treated cells when compared to untreated cells.