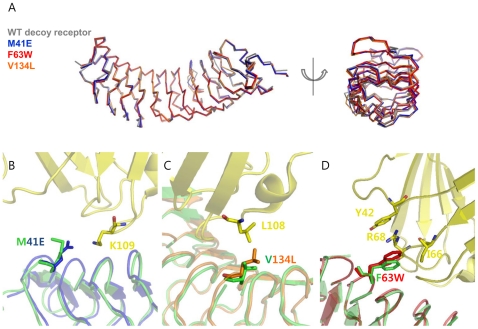
Figure 3. Interface structures of single variants.
(A) Superimposed backbone structures of the wild-type decoy receptor and three single mutants (M41E, F63W, and V134L). (B) Interface structure of the M41E mutant obtained by superimposing the crystal structure of apo M41E mutant into the wild-type decoy receptor/MD2 complex structure. Glu-41 was positioned to be able to form a salt-bridge with Lys-109 on MD2. The crystal structure of the M41E is shown in blue, and the wild-type decoy receptor and MD2 are colored in green and yellow, respectively. (C) Interface structure of the V134L mutant obtained by superimposing the crystal structure of apo V134L mutant into the wild-type decoy receptor/MD2 complex structure. The larger Leu-134 is possible to make closer contact with Leu-108 on MD2. The crystal structure of the V134L is colored in orange (D) Interface structure of the F63W mutant obtained by superimposing the crystal structure of apo F63W mutant into the wild-type decoy receptor/MD2 complex structure. The mutated Trp-63 was expected to create the amino-aromatic (cation-π) interaction of Tyr-42 and Arg-68. The crystal structure of the F63W is shown in red.