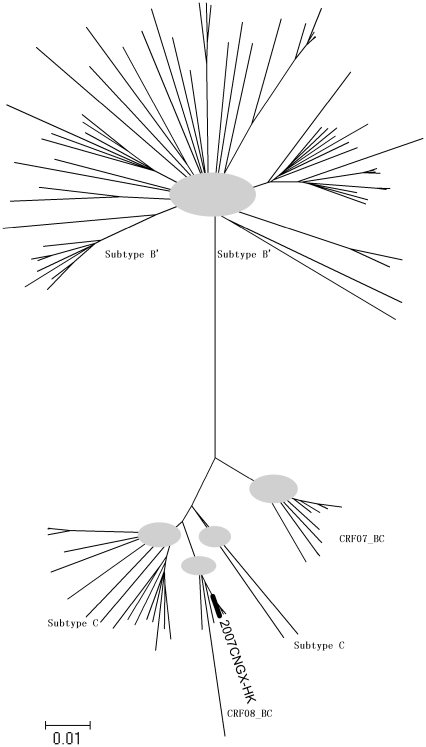
Figure 7. Phylogenetic reconstruction of HIV-1 subtypes and recombinants of Asian origin.
A phylogenetic tree was generated from sequence alignments, and plotted using a neighbor-joining method. This was analysis implemented in MEGA 5 [35], [36] using 1000 bootstrap replicates. The optimum tree, with the sum of branch length equal to 2.05356961 is displayed. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method, available as a public software tool (http://www.megasoftware.net/WebHelp/part_iv___evolutionary_analysis/computing_evolutionary_distances/distance_models/nucleotide_substitution_models/hc_mcl.htm). The analysis included 113 nucleotide sequences in toto. Reference HIV-1 genomic sequences of subtypes B, C, 07BC and 08BC were used, and are available from the Los Alamos National Library (LANL). All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated (gap-stripped) as per the software algorithm. The 2007CNGX-HK genome formed a clade with the other CRF_08BC isolates. The grey circles indicate the junctions of the branches having close phylogenetic relationships.