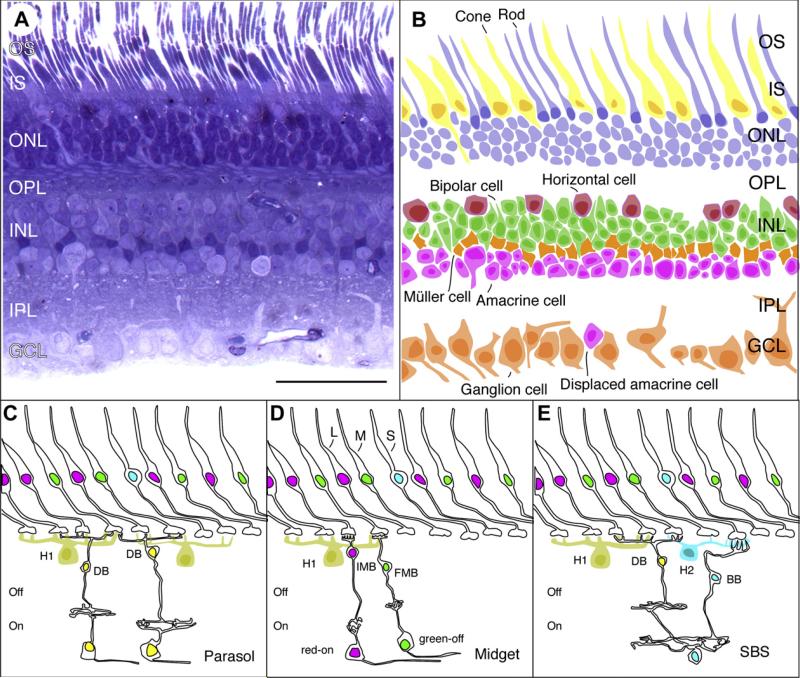
Fig. 1.
Moving from histology to functional circuitry in primate retina. Scale bar (50 μm) in A applies to all panels allowing relative size and disposition of neuron populations to be compared. A, semithin radial section through macaque monkey retina. Toluidine blue (Nissl) stain near 3 μm eccentricity. OS, outer segments; IS, inner segments; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. B, disposition of neuron populations in the same area. Silhouettes show cell somata and nuclei visible in the section from panel A; inner and outer segments of some rod and cone receptors are also drawn. C, parasol pathway. Excitation to off-parasol cells is through several flat diffuse bipolar cells (only one is shown); excitation to on-parasol cells is through invaginating diffuse bipolar cells. Surround inhibition to diffuse bipolar cells derives from H1 class of horizontal cells in OPL; additional inhibition may be present in IPL (not drawn). H1, horizontal cell; fdb, flat diffuse bipolar cell; idb, invaginating diffuse bipolar cell. D, midget pathway. Excitation to midget ganglion cells is through single-cone contacting midget bipolar cells; Surround inhibition to midget bipolar cells derives from H1 class of horizontal cells in OPL; additional inhibition may be present in IPL (not drawn). imb, invaginating midget bipolar cell; fmb, flat midget bipolar cell. L, long wavelength-sensitive cone; M, medium wavelength sensitive cone. S, short-wavelength sensitive cone. E, small bistratified (“blue-on”) pathway. On-sign excitation to blue-on cells from S cones is through blue cone bipolar cells. Off excitation from ML cones is through diffuse bipolar cells. Inhibition is from H2 class of horizontal cells in the OPL to S cones and from H1 horizontal cells to ML cones.