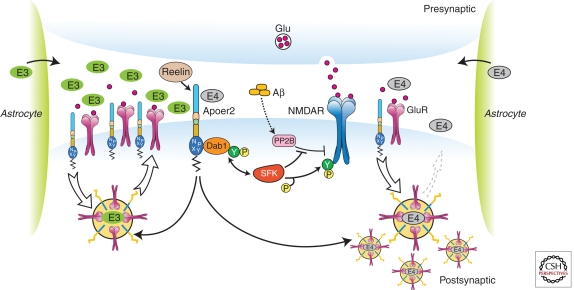
Figure 3.
ApoE isoforms differentially impair ApoE receptor and glutamate receptor recycling at the synapse. Apoer2 induces N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) tyrosine phosphorylation by activating Src family tyrosine kinases (SFKs) in response to Reelin in the postsynaptic neuron. Astrocyte-derived ApoE3 (green ovals) or ApoE4 (gray ovals) bind to Apoer2 and are constitutively but slowly internalized. Apoer2 undergoes accelerated endocytosis in response to Reelin signaling. ApoE4 sequesters Apoer2 in intracellular compartments along with glutamate receptors (NMDAR and GluR), thereby reducing the ability of the postsynaptic neuron to recycle these proteins with normal kinetics, whereas ApoE2 or ApoE3 efficiently recycle back to the cell surface and thus deplete surface Apoer2 and glutamate receptor levels to a lesser extent (illustrated on the left for ApoE3). Aβ oligomers interfere with NMDAR tyrosine phosphorylation by activating tyrosine phosphatases (Snyder et al. 2005). (Modified from Chen et al. 2010; reprinted, with permission, from the National Academy of Sciences © 2010.)