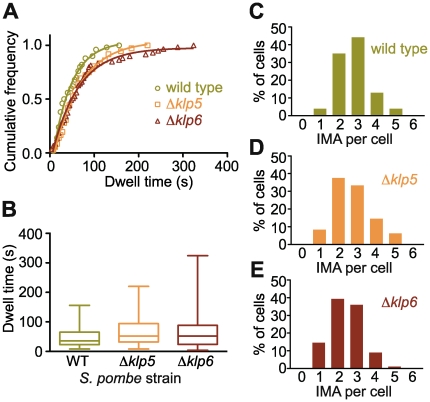
Figure 7. Deletion of klp5 or klp6 increases microtubule dwell time in vivo.
Time-lapse movies (Movies S3, S4, S5, S6) of GFP-microtubules in live wild type (wt), klp5 or klp6 deletion mutant S. pombe were analysed and the dwell time of microtubules in contact with the cell wall before undergoing catastrophe recorded. (A) Cumulative frequency plots of dwell times were each fitted with a single exponential. The half-lives of the dwell time were significantly longer in Δklp5 (42 s) and Δklp6 (42 s) cells compared to wild type (29 s, p<0.05). (B) Box and whisker plots for the microtubule dwell time data plotted in (A) showing median and interquartile range (box) and distribution limits (whiskers). Median values are wt: 36 s, Δklp5: 52 s and Δklp6: 52 s. Deletion of klp6 decreases IMA number in vivo. Normalised frequency distribution plots for IMA number per S. pombe cell in wild type (WT, C), Δklp5 (D) and Δklp6 (E) strains. Mean numbers of IMA per cell were wild type: 2.8±0.1 (mean ± SEM, n = 77); klp5 deletion: 2.7±0.1 (n = 48); klp6 deletion: 2.4±0.1 (n = 89). The reduction in IMA number in klp6 deletions compared to wild type is significant with P = 0.01.