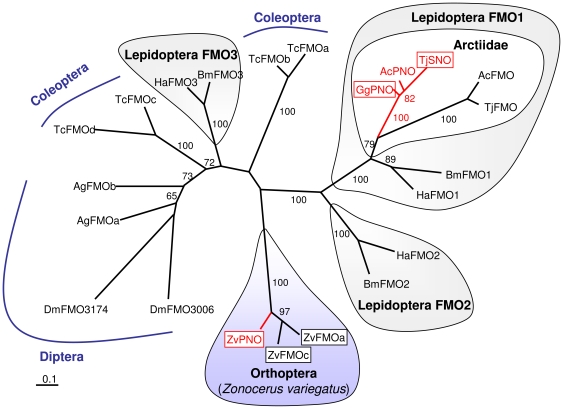
Figure 2. Unrooted maximum-likelihood tree of amino acid sequences derived from cDNA encoding FMOs of various insect species.
Framed sequences were heterologously expressed and functionally analyzed. The other sequences should be regarded as putative FMO-coding cDNA. Branch lengths are proportional to the number of amino acid substitutions per site (scale: 0.1 substitutions per site). Bootstrap proportions resulted from 1000 replicates and are given for values >50. Ac, Arctia caja; Ag, Anopheles gambiae; Bm, Bombyx mori; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; Gg, Grammia geneura; Ha, Helicoverpa armigera; Tc, Tribolium castaneum; Tj, Tyria jacobaeae; Zv, Zonocerus variegatus. Accession numbers for all sequences are listed in Figure S1.