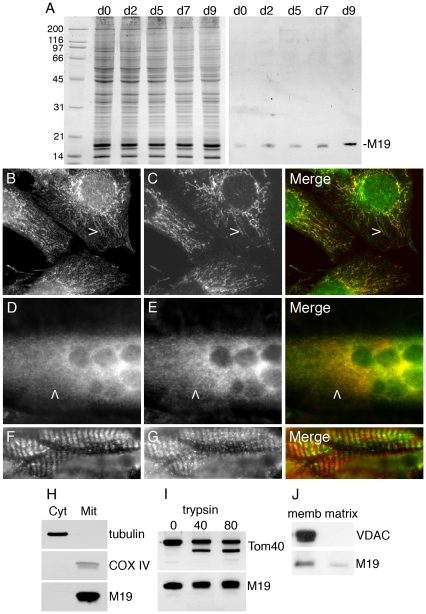
Figure 1. Expression and localization of M19 in muscle cells.
(A) Coomassie-blue stained gel and Western blot analysis of M19 in extracts from C2C12 cells grown in proliferation medium (d0) or placed in differentiation-promoting conditions for 2 to 9 days (d2 to d9). M19 is detected by the rabbit polyclonal P70612 antibody. (B, C) C2C12 myoblasts were grown in proliferation medium or (D, E) were placed in differentiation medium for 6 days, and then were double-labeled with the specific P70612 antibody (B, D; green) and an anti-cytochrome c antibody (C, E; red). There is a co-localization between the 2 detected proteins in C2C12 myoblasts (B, C, merge) and myotubes (D, E, merge) as indicated by arrowheads. (F, G) Double-label indirect immunofluorescence of mouse Tibialis anterior sections showing M19 (F; green) and cytochrome c (G; red). (H) After C2C12 cell fractionation, proteins from the cytosolic and the mitochondria fractions were separated by SDS-PAGE. Tubulin, COX IV and M19 are detected by Western immunobloting. (I) Purified mitochondria are subjected to limited degradation using increasing concentration of trypsin, from 0 to 80 µg/ml. The mitochondria are then lysed in Laemmli buffer. Tom40 and M19 are detected by Western immunobloting. (J) Purified mitochondria are disrupted with freeze/thaw cycles, followed by Na2CO3 precipitation. After centrifugation, the membrane fraction (memb) and the matrix/intermembrane space fraction (matrix) are analyzed by Western immunobloting using a VDAC antibody and the P70612 antibody.