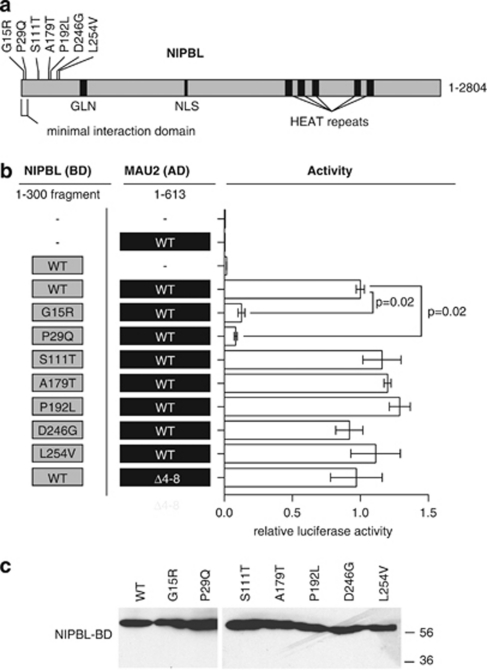
Figure 2.
The effect of NIPBL mutations on NIPBL/delangin–MAU2 interaction. (a) NIPBL/delangin motifs include a glutamine-rich domain (GLN), nuclear localization signal (NLS) and HEAT-repeat motifs. The minimal MAU-2 interaction fragment used (aa 1–38) and relative positions of mutations tested are demonstrated. (b) Constructs tested are indicated in the right panel and interaction data from mammalian two-hybrid assays are indicated in relative luciferase units for each CdLS mutation tested at the left. Significance of difference in activity of the G15R and P29Q versus wild-type (WT) are indicated. (c) Western blotting of NIPBL-BD 1–300 fragments with missense mutations from two-hybrid assays, using anti-GAL4 (DBD) antibody (Santa Cruz). All proteins are expressed at similar levels.