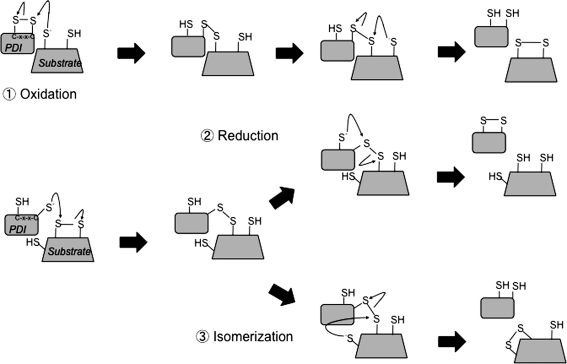
FIG. 2.
Thiol–disulfide exchange reactions between protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) proteins and substrates. (1) Oxidation. Oxidized PDI engages reduced substrate and allows for a mixed disulfide to form between PDI and the substrate. This mixed disulfide is resolved by a nucleophilic attack of a cysteine residue's thiolate anion on the substrate. This reaction results in oxidized substrate and reduced PDI. (2) Reduction. Reduced PDI forms a mixed disulfide bond with an oxidized substrate, which is resolved by a cysteine residue on PDI and results in oxidized PDI and reduced substrate. (3) Isomerization. Reduced PDI again forms a mixed disulfide with a substrate but instead is resolved by a cysteine residue on the substrate forming a different disulfide bond. This reaction results in reduced PDI and isomerized substrate.