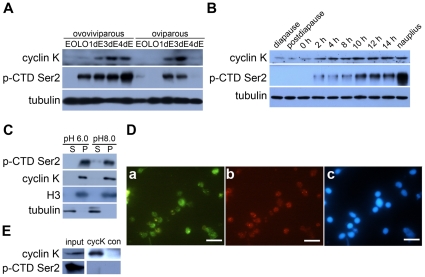
Figure 3. Cyclin K protein expression and phosphorylation of RNAP II in different developmental phases and their subcellular localization in Artemia embryos.
(A) Cyclin K protein expression and CTD Ser2 phosphorylation of RNAP II in the two developmental pathways. EO, early oocytes; LO, late oocytes; 1dE, 3dE and 4dE represent embryos entering uterus for 1 day, 3 days and 4 days, respectively. (B) Cyclin K protein expression and CTD Ser2 phosphorylation of RNAP II during the hatching process of diapause embryos (includes diapause embryo, postdiapause embryo, 0- to 14-h incubated embryos and nauplius); α-tubulin was used as a loading control. (C) Supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions were prepared using buffer K (pH 6.0 or 8.0) from 14-h incubated embryos. Cyclin K and CTD Ser2 phosphorylation of RNAP II were detected by Western blotting. Tubulin and H3 were also examined to indicate the purity of the different extracts. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of nuclei from 14-h incubated embryos confirmed that cyclin K co-localizes with phosphorylated RNAP II in nuclei. a, cyclin K; b, phosphorylation of CTD Ser2; c, DAPI stain. The bars represent 10 µm. (E) Cyclin K and its associated factors (anti-cyclin K immunoprecipitates) were affinity purified from the 14-h incubated embryos and analysed by western blot. Another polyclonal antibody produced in rabbit (anti-SGEG2a) was used in a parallel procedure for control (con). The input loading quantity was 1/100 of the total supernatants.