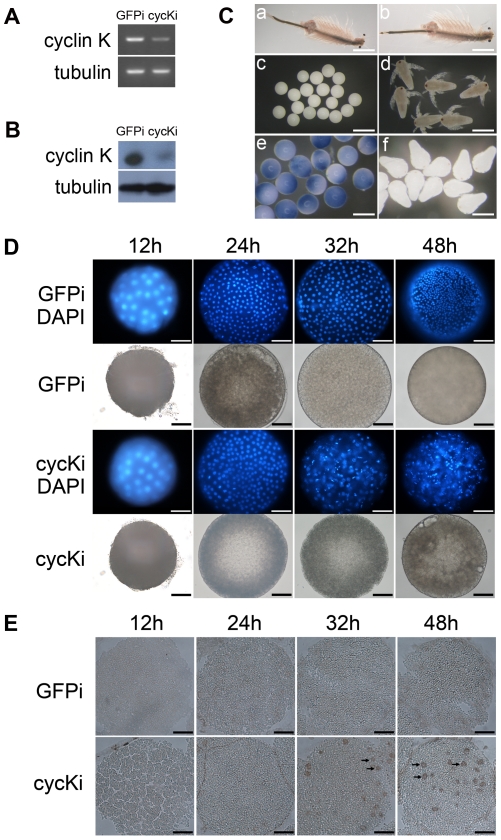
Figure 5. Knockdown of cyclin K in developing embryos.
(A) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of cyclin K mRNA levels in control (GFPi) and test (cycKi) groups. (B) Western Blot analysis of cyclin K protein levels in control (GFPi) and test (cycKi) groups. (C) Morphology of adult Artemia: cyclin K RNAi (a) and GFP RNAi (b); Offspring produced by cyclin K RNAi (c) and GFP RNAi (d) Artemia; Trypan Blue staining of embryos entering utrus for four days reproduced by cyclin K RNAi (e) and GFP RNAi (f) Artemia. The bars in (a) and (b) represent 30 mm. The bars in (c) represent 215 µm. The bars in (d–f) represent 150 µm. (D) DAPI staining of early development embryos. The samples are eggs having entered the uterus for 12, 24, 32 and 48 h respectively. The upper two panels are GFP RNAi groups (GFPi); the lower two panels are cyclin K RNAi groups (RNAi). (E) TUNEL assay of embryos at the same stages of development as shown in D, 8-µm frozen sections were prepared and DNA strand breaks were detected by the TUNEL assay. Arrows indicated positive signals in cyclin K RNAi embryos. The bars in both (D) and (E) indicate 35 µm.