Figure 2.
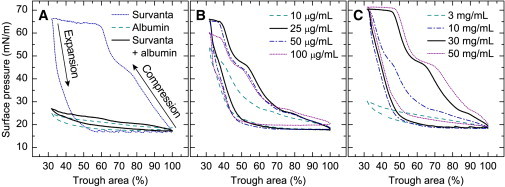
Third-cycle isotherms at 25°C demonstrate the normal, inhibited, and polymer-restored activity of Survanta. (A) Survanta (dotted line) deposited dropwise in a physiological, buffered-saline subphase. The maximum surface pressure was > 65 mN/m (surface tension < 10 mN/m) upon compression, with significant hysteresis upon expansion. For a subphase containing albumin (dashed line), there were minimal changes in surface pressure with changes in interfacial area, consistent with the expected desorption-adsorption behavior of the soluble, surface-active albumin. When Survanta was added to a subphase containing albumin (Survanta + albumin, solid black line), the isotherm nearly matched that of pure albumin. (B) Survanta added to subphases containing albumin and a series of chitosan concentrations. Increasing chitosan concentrations first restored the normal Survanta isotherm, but then caused less Survanta to adsorb and the maximum surface pressure to decrease. (C) Survanta added to subphases containing albumin and a series of PEG concentrations. Increasing the PEG concentration restored the normal Survanta isotherm.
