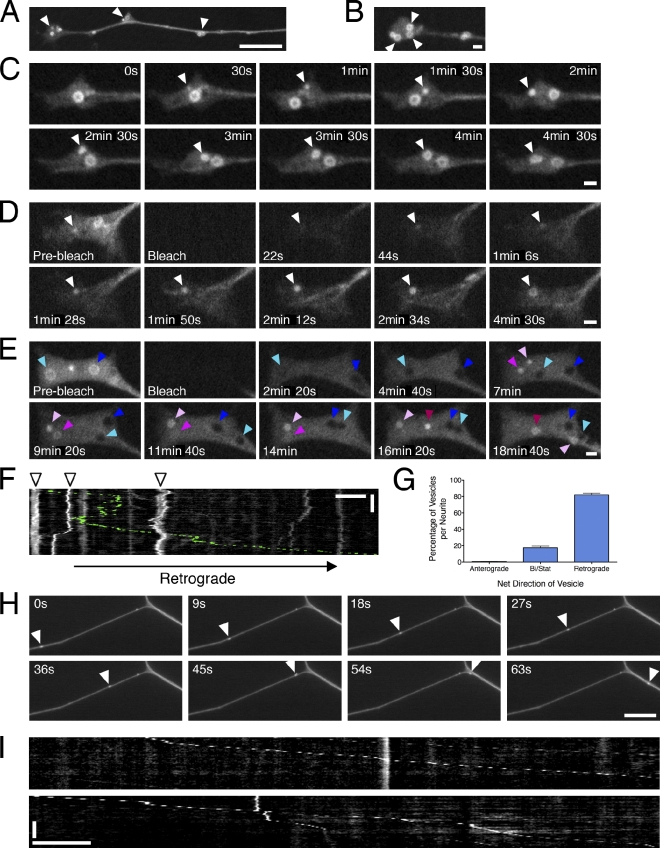
Figure 1.
Autophagosomes initiate distally and undergo retrograde movement toward the cell soma in primary neurons. (A) GFP-LC3 localization at the distal end of DRG neurons. Arrowheads denote the accumulation of GFP-LC3–positive puncta. (B) Autophagosomes initiate in the distal tip of the neurite, where pronounced ringlike structures accumulate (arrowheads). (C) Time series of autophagosome biogenesis; arrowheads denote the appearance and growth of GFP-LC3–positive puncta into a ring (Video 1). (D and E) FRAP analysis of the distal neurite. Open arrowheads denote recovering puncta and growth into a ring, cyan and dark blue arrowheads denote two different examples of black holes of bleached preexisting rings, three different pink-shaded arrowheads denote the appearance of three different GFP-LC3–positive puncta that grow into rings. (F) Kymograph of autophagosome motility in the distal neurite showing bidirectional movement within a constrained region (arrowheads). Occasional autophagosomes escape from the tip and move processively toward the cell soma (retrograde track is pseudocolored green; Video 2). (G) Percentage of retrograde, anterograde, or bidirectional/stationary (Bi/Stat) vesicles (means ± SEM; n = 91 neurites). (H and I) Times series and corresponding kymographs showing processive movement of GFP-LC3–positive puncta along the axon (Video 3). Arrowheads denote an autophagosome traveling along the axon toward the cell soma. Retrograde motility is toward the right in all figures. Horizontal bars: (B–E) 1 µm; (A, F, H, and I) 10 µm. Vertical bars: (F) 2 min; (I) 1 min.