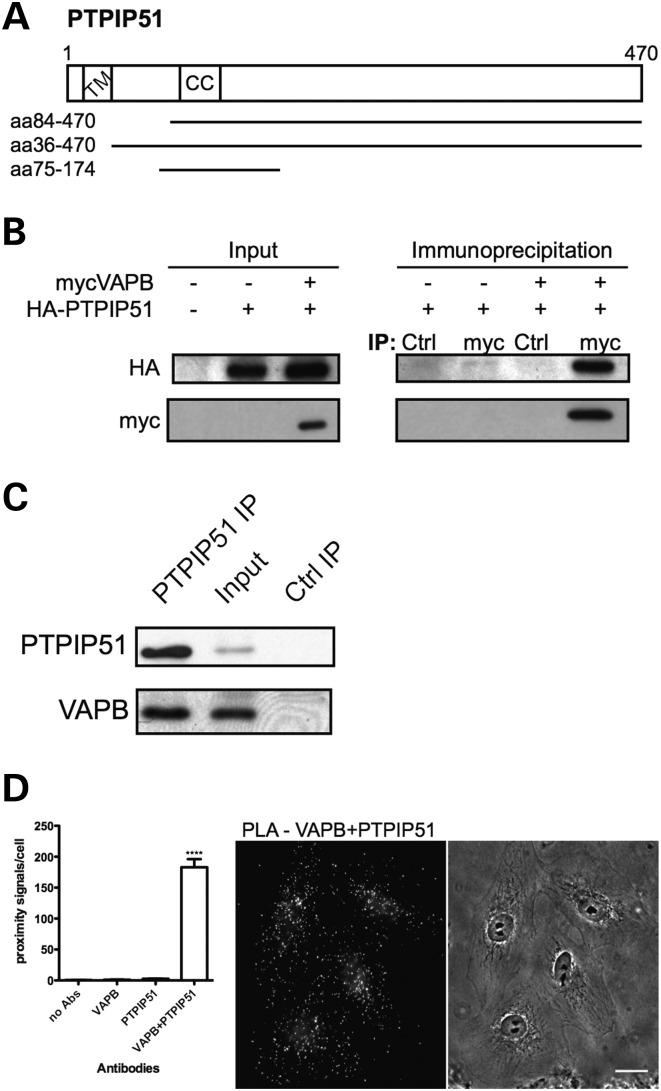
Figure 1.
VAPB interacts with PTPIP51. (A) Domain structure of PTPIP51. CC, coiled coil domain; TM, transmembrane domain. The VAPB-interacting PTPIP51 clones identified by yeast two-hybrid are indicated. (B) Myc-VAPB and HA-PTPIP51 co-immunoprecipitate in transfected HEK293 cells. Myc-VAPB was immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibody from cells transfected with myc-VAPB and/or HA-PTPIP51. Non-immune mouse antibody was used as control (Ctrl). The immune pellets were probed for myc-VAPB (Myc) and HA-PTPIP51 (HA) on immunoblots. The input levels of myc-VAPB and HA-PTPIP51 in the transfected cells are shown (input). (C) Endogenous PTPIP51 and VAPB co-immunoprecipitate in HEK293 cells. PTPIP51 was immunoprecipitated using rat anti-PTPIP51 antibody (PTPIP51 IP) and the immune pellet probed for VAPB and PTPIP51 on immunoblots with rabbit VAPB (#3504) and PTPIP51 (FAM82A2) antibodies, respectively; immunoprecipitation with pre-immune rat serum was used as a control (Ctrl IP). A sample of the input lysate is also shown. (D) Quantification of in situ proximity ligation assay results (mean ± SEM). Cells were probed with no primary antibodies (no Abs) (n = 10), with VAPB antibody only (VAPB) (n = 10), with PTPIP51 antibody only (PTPIP51) (n = 10) and with VAPB+PTPIP51 antibodies (n = 32) and the numbers of signals/cell determined. Representative VAPB+PTPIP51 labelling with corresponding phase contrast image are shown (scale bar, 20 μm).