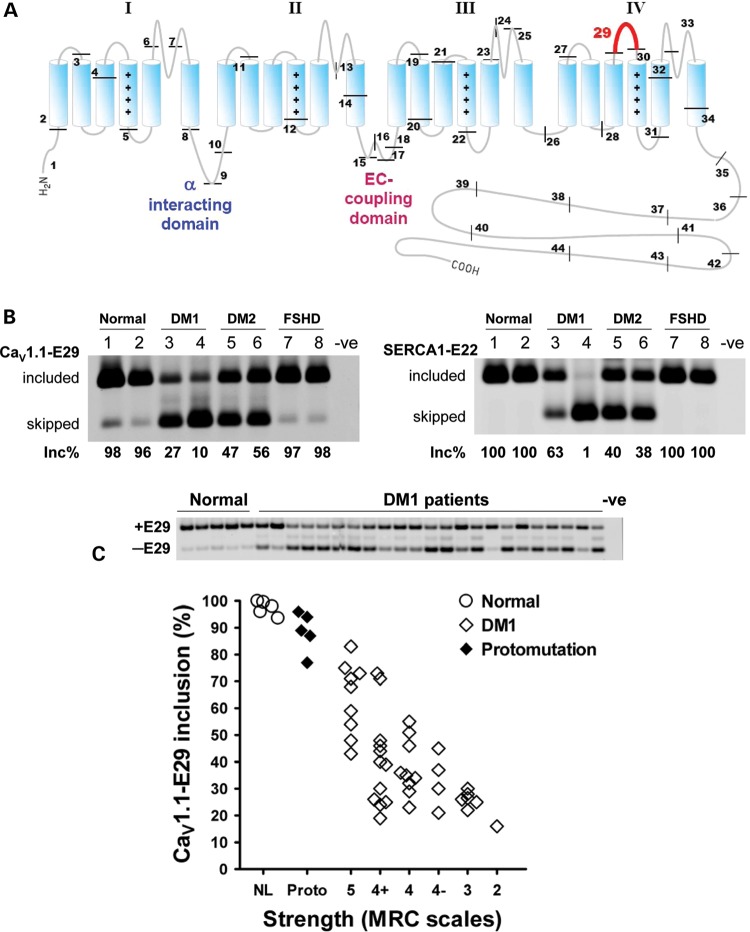
Figure 1.
Correlation of CaV1.1 E29 skipping and muscle strength in DM. (A) Schematic representation of CaV1.1 topology and exon organization. CaV1.1 is composed of four membrane-spanning repeat domains (I–IV). Each repeat consists of six transmembrane segments (S1–S6). The protein segment encoded by the alternatively spliced E29 (57 nts, highlighted in red) is located in the IVS3–IVS4 extracellular loop. Positive charges in the S4 segments of each repeat are indicated by ‘+’ symbols. Locations of the α interacting domain in the I–II loop, which binds the β1α subunit, and the EC coupling domain in the II–III intracellular loop, are also indicated. (B) RT–PCR assay for alternative splicing of CaV1.1 E29 (CaV1.1-E29, left) and SERCA1 exon 22 (SERCA1-E22, right) in muscle from normal (lanes 1 and 2), DM1 (lanes 3 and 4), DM2 (lanes 5 and 6) and FSHD (lanes 7 and 8) individuals. Inc% denotes the fractional inclusion rate, calculated as the signal intensity of inclusion (upper) band divided by the summed intensities of the corresponding inclusion and exclusion (lower) bands. Negative control (-ve) refers to the absence of template. (C) Upper panel shows representative RT–PCR E29 inclusion results for several normal (lanes 1–5) and DM1-affected (lanes 6–28) individuals. Negative control (-ve) refers to the absence of template. Lower panel shows correlation of ADF strength with fractional E29 inclusion in TA muscles from healthy individuals (n = 5, ‘NL’), DM1 protomutation (n = 5, ‘Proto’) and classical DM1 (n = 41). Strength was determined by standardized manual muscle testing using Medical Research Council scales (46). An MRC scale value of 5 indicates normal strength, 4 indicates moderate weakness, 3 indicates full active range of movement against gravity with no added resistance and 2 indicates inability to dorsiflex fully against gravity. The Spearman rank correlation for E29 inclusion versus strength in classical DM1 was r = 0.6560 (P < 0.0001, excludes normal and protomutation subjects).