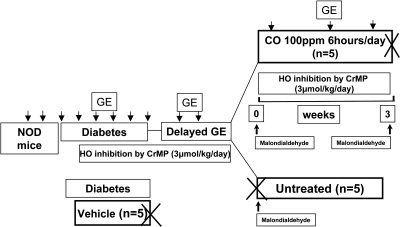
Fig. 2.
Cartoon of experimental plan for CO inhalation with heme oxygenase (HO) inhibition. Eight-week-old female NOD/ShiLtJ mice were received from Jackson laboratory, and 2 baseline gastric emptying readings were obtained before the mice became diabetic. After development of diabetes, gastric emptying was measured weekly. After 2 wk of diabetes, mice either received daily intraperitoneal injections of chromium mesoporphyrin (CrMP), 3 μmol/kg per day dissolved in 0.25% ammonium hydroxide (n = 10), or daily intraperitoneal injections of 0.25% ammonium hydroxide (Vehicle; n = 5). All mice injected with CrMP developed delayed gastric emptying as confirmed by 2 consecutive gastric emptying readings; all mice injected with ammonium hydroxide alone had normal gastric emptying. Mice with delayed gastric emptying were either killed soon after development of delayed gastric emptying (n = 5), and serum was collected, or they were assigned to receive CO inhalation (100 ppm for 6 h/day) for a maximum period of 8 wk or less if the mouse had 2 consecutive normal gastric emptying t1/2 (n = 5). These mice continued to receive daily intraperitoneal injections of CrMP to continually inhibit HO activity. At the end of this period the mice were killed and serum was collected.