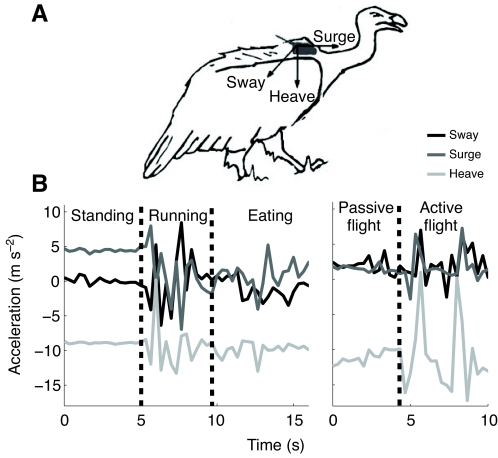
Fig. 2.
(A) Schematic representation of a tri-axial accelerometer attached to a vulture, recording linear acceleration along the x (medial–lateral, sway), y (anterior–posterior, surge) and z (inferior–superior, heave) axes. (B) Two illustrative signals recorded by a tri-axial accelerometer (3.3 Hz per axis), demonstrating switches from standing through running to eating and from passive to active flight.