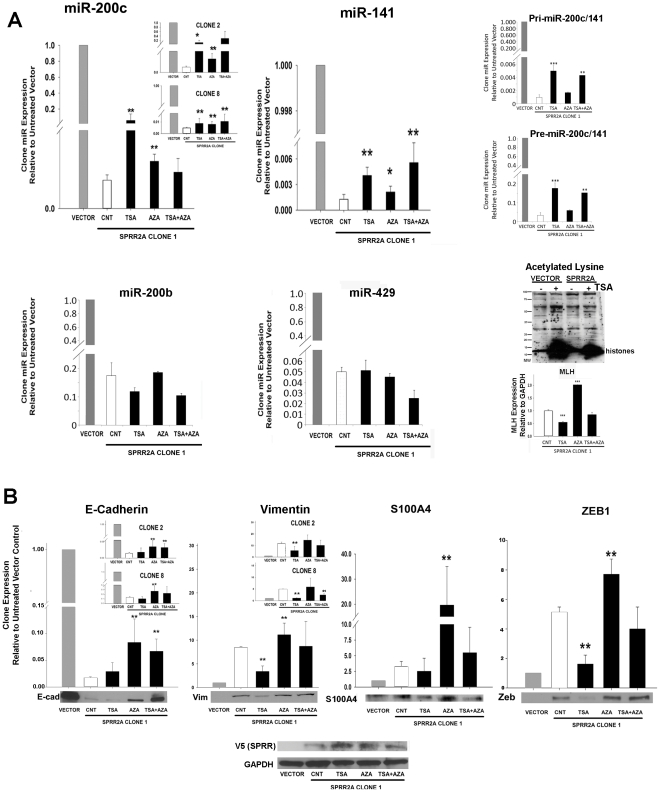
Figure 2. In mesenchymal HuCCT-1 SPRR2a cells, acetylation can cause epithelial shifts in miR200c/141, vimentin and Zeb1 expression.
De-methylation has less impact on miR200c/141 transcription, but does affect EMT marker protein expression. In HuCCT-1 SPRR2a cells, TSA yields a greater epithelial shift in miR200c/141 expression than AZA, while miR200b/a/429 is unaffected (A). TSA increased expression levels for both primary miR-200c/141 and premature miR-200c transcripts as well (A). The efficacy of TSA/AZA treatment was monitored by western blot for acetylated lysine (TSA) and real time PCR for MLH expression (AZA) (A). Expression levels of EMT markers (both mRNA and protein) showed that TSA also reduced expression of vimentin and Zeb1 in SPRR2a cells (partial MET shift), while AZA treatment increased expression of all markers tested (B). Finally, SPRR2a over expression was maintained during TSA/AZA treatment (B). Real time PCR analysis: comparative 2−ΔΔCT method (U6 or GAPDH internal control) and expression levels for HuCCT-1-vector cells were set to 1.0. (n≥3 independent experiments; *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***,P<0.005; Student's t-test).