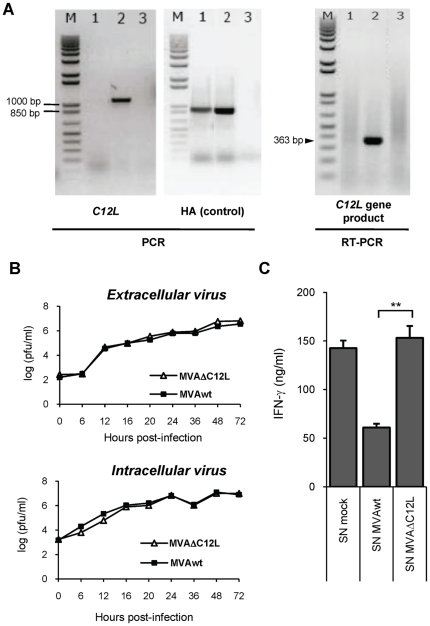
Figure 1. In vitro characterization of MVAΔC12L.
(A) Corroboration of correct C12L gene deletion and abrogation of IL-18 bp expression. DNA and total RNA were extracted from CEFs infected with MVAΔC12L, MVAwt or mock-infected cells (lanes 1, 2 and 3 respectively). C12L (left) and HA (control gene, middle) sequences were amplified by PCR using specific primers. Absence of C12L mRNA (right) was assessed by RT-PCR using specific primers. M: molecular weight marker (1 kb plus DNA ladder, Invitrogen). (B) Analysis of virus growth in CEFs after infection at low moi (0.01 pfu/cell), with MVAΔC12L (white triangles) or MVAwt (black squares). Quantification of extra (upper panel) and intracellular (lower panel) virus yields at the different indicated time points was performed as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Inhibition of mouse IL-18 biological activity. To evaluate the inhibition of the IL-18-induced IFN-γ production, mice naïve splenocytes were treated with Con A (200 ng/ml) and rIL-18 (5 ng/ml) in the presence of supernatants (SN) from 105 CEFs that had been mock-infected or infected with the indicated viruses. The level of IFN-γ in the culture SN was determined by a standard ELISA assay 24 hs later. Statistically significant differences between MVAwt and MVAΔC12L: **p<0.01.