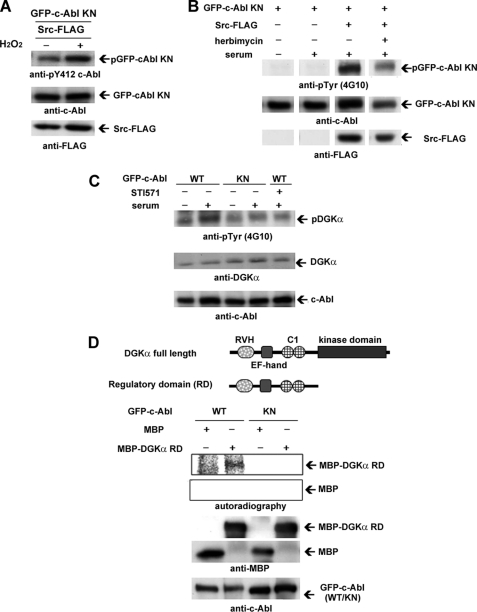
FIGURE 4.
c-Src activated in a serum-dependent manner phosphorylates c-Abl, resulting in the subsequent phosphorylation of DGKα. A, H2O2-induced activation of c-Abl by c-Src. GFP-c-Abl kinase-negative (KN) and FLAG-tagged c-Src (Src-FLAG) were co-transfected into COS-7 cells as described under “Experimental Procedures.” After a 30-min incubation with 3 mm H2O2, the transfected cells were harvested and homogenized. The lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting using anti-Tyr(P)-412-c-Abl, anti-c-Abl, and anti-FLAG antibodies. B, serum-induced activation of c-Abl by c-Src. GFP-c-Abl KN and c-Src-FLAG (Src WT) or kinase-negative FLAG-Src (Src KN) were co-transfected into NIH3T3 cells by lipofection. After serum starvation for 24 h, the cells were preincubated with herbimycin for 15 min, followed by incubation with fresh medium containing serum with 1 μm herbimycin for 30 min. The homogenate of the cells was subjected to immunoblotting analysis using anti-Tyr(P) (4G10 antibody), anti-c-Abl, and anti-FLAG antibody. Images cut out from one gel are put together because the order was different. C, tyrosine phosphorylation of endogenous DGKα serum-activated c-Abl. After 24 h of serum starvation, NIH3T3 cells expressing GFP-c-Abl were preincubated with 5 μm STI571 for 15 min, followed by further treatment with serum and 5 μm STI571 for 30 min. The lysates were subjected to immunoblotting analysis using anti-Tyr(P), anti-DGKα, and anti-c-Abl antibodies. D, direct phosphorylation of DGKα by c-Abl. An in vitro c-Abl kinase assay was carried out using purified MBP-DGKα regulatory domain and immunoprecipitated GFP-c-Abl or GFP-c-Abl KN. Purified MBP was used as a control. The reaction products were subjected to immunoblotting analysis using anti-MBP and c-Abl antibodies, and radioactive signals were detected by BSA2500. Schematic representations of DGKα regulatory domains are shown at the top. Error bars, S.E.