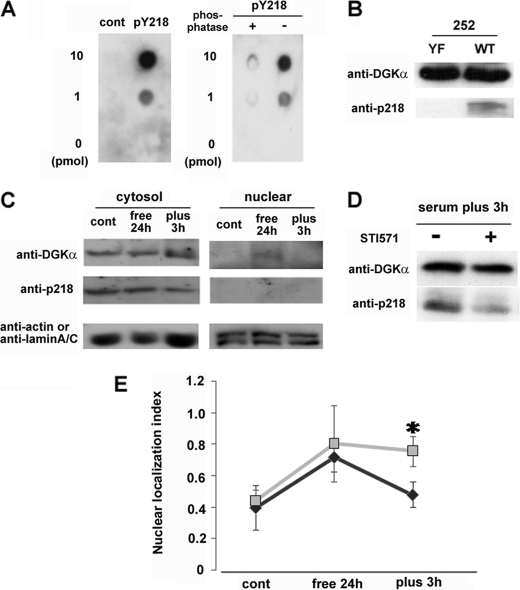
FIGURE 6.
Tyr-218 is phosphorylated in vivo and necessary for the serum-induced nuclear export of DGKα. A, specificity of anti-phospho-Tyr-218 of DGKα. The indicated amount of the antigen peptide (FPRPVpYVNLCE), control peptide corresponding to a different part of DGKα (CQKYMEpYSTKKV), or dephosphorylated antigen peptide was dotted on the PVDF membrane. Immunostaining was performed using purified anti-phospho-Tyr-218 antibody (500× dilution). B, detection of phospho-Tyr-218 in vitro. The peptide 252 with (YF) or without (WT) the point mutation at Tyr-218 described in the legend to Fig. 5B was phosphorylated by v-Abl in vitro and then applied to SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting using the Tyr(P)-218 antibody. The WT 252 peptide, but not the YF mutant, was detected by the antibody, indicating that the antibody specifically recognized the phospho-Tyr-218. C, detection of phospho-Tyr-218 in vivo. Before and after serum starvation and after 3 h of serum restoration, NIH3T3 cells were harvested and fractionated as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The cytosolic fraction (50 μg) and nuclear fraction (75 μg) were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunostaining using anti-DGKα, Tyr(P)-218, actin, and lamin A/C antibodies. D, effect of STI571 on the serum-induced phosphorylation of endogenous DGKα at 218. After 24 h of serum starvation, NIH-3T3 cells were cultured with (+) or without (−) 20 μm STI571 in the normal medium for 3 h. The cells were harvested, and total lysate (100 μg) was subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunostaining using anti-DGKα and Tyr(P)-218 antibodies. E, effect of Tyr-218 mutation on the serum-induced nuclear export of DGKα. Cells expressing GFP-DGKα or the Y218F mutant were exposed to 24-h serum starvation, and the medium was then changed to one containing serum. The transfected cells were fixed before and after serum depletion and 3 h after serum restoration and categorized into three groups as described in the legend to Fig. 1A. *, p < 0.05. n = 100 × 3. Error bars, S.E.