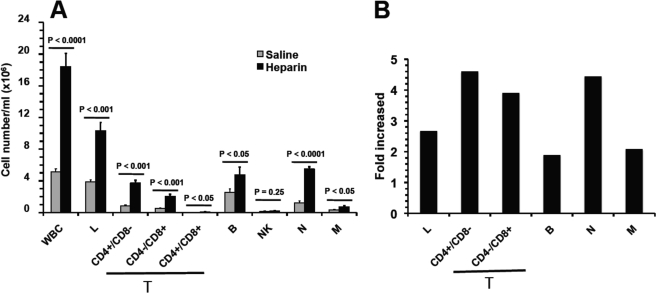
FIGURE 1.
Heparin-induced leukocytosis is mainly attributable to lymphocytosis and neutrophilia. A and B, subpopulation distribution of leukocytes in cell numbers (A) and alteration in ratios over saline control (B). The leukocytosis is mainly attributable to a massive increase of circulating lymphocytes (lymphocytosis) and neutrophils (neutrophilia), which account for roughly 62 and 33% of the total leukocyte elevation in peripheral blood, respectively. The data were summarized from three sets of experiments with 8–12 mice per group. Each bar represents the average value ± S.E. The statistical analysis was carried out by paired Student's t test in comparison with saline treatment. WBC, white blood cells; L, lymphocytes; M, monocytes; N, neutrophils; T, T lymphocytes; B, B lymphocytes.