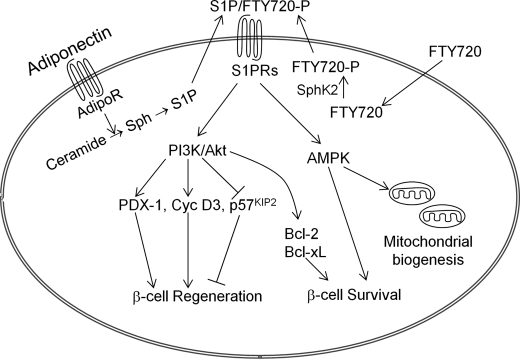
FIGURE 11.
Proposed mechanism for FTY720-stimulated β-cell regeneration in vivo. S1P signaling is a core component of the adiponectin-mediated pleiotropic actions (54). Binding of adiponectin to its receptors enhances deacylation of ceramide to sphingosine, which can then be phosphorylated to form S1P (54). FTY720, a structural analog of sphingosine, is phosphorylated in vivo to form FTY720-P (25). Inside-out signaling of S1P/FTY720-P via S1P receptors activates the PI3K/Akt pathway, which leads to up-regulation of PDX-1 and cyclin D3 and down-regulation of p57KIP2, and subsequently β-cell regeneration in vivo. FTY720 also promotes cell survival through activation of PI3K/Akt (38) and expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. In addition, S1P receptor signaling plays a key role in adiponectin-mediated AMP-activated protein kinase activation, which is important for mitochondrial biogenesis and β-cell survival (54). Thus, FTY720 acts on an intrinsic pathway that is physiologically important for β-cell regeneration and survival under metabolic stress. Sph, sphingosine; S1PRs, S1P receptors; AdipoR, adiponectin receptors.