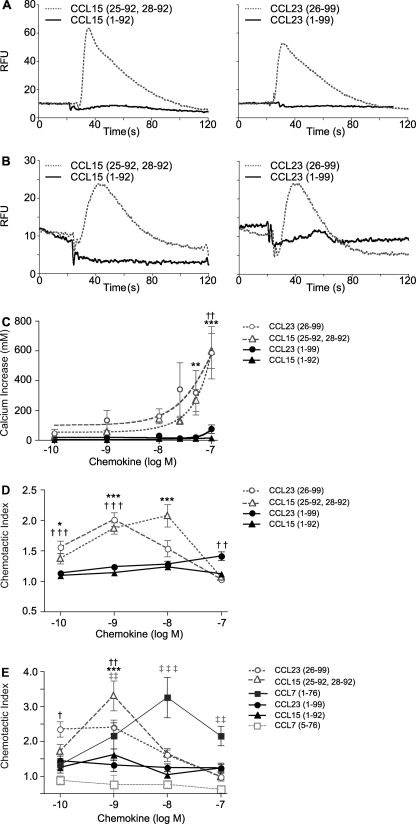
FIGURE 6.
MMP-mediated cleavages of CCL15 and CCL23 activates chemokine agonism. Calcium mobilization (A–C) and chemotactic potential (D–E) of CCL15 and CCL23 are enhanced by MMP processing. A and B, representative traces of calcium flux, shown as a burst in relative fluorescence units (RFU) after the addition of 10 nm of full-length or MMP-truncated chemokine in CCR1-transfected B300-19 (A) and THP-1 cells loaded with Fluo-4 calcium indicator reagent (B). C, shown is the calcium mobilization dose response of THP-1 cells wherein calcium concentrations were calculated from relative fluorescence based on calibration with ionomycin and MnCl2. Transwell migration of CCR1-transfected B300-19 for 3 h (D) or THP-1 cells for 90 min (E) toward full-length or truncated chemokine through a 5-μm pore-sized filter is shown. Migrated cells were quantified by CyQUANT assay and displayed as chemotactic index, defined as the ratio of cells migrating in response to stimulus compared with buffer control. Results shown are the mean ± S.E. of three or more biological replicates of experiments completed in quadruplicate. Statistical analysis was by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test; the levels of significance comparing full-length to MMP-cleaved counterpart are: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.