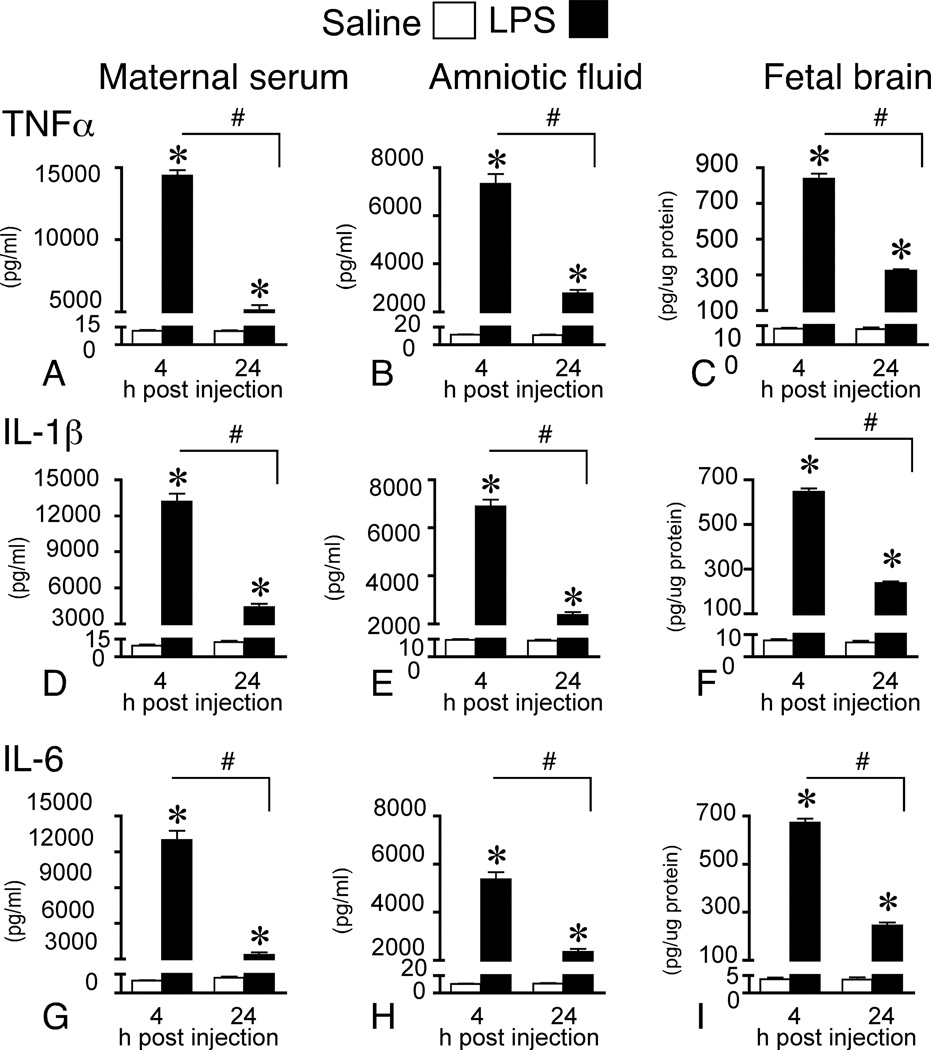
Figure 1.
Maternal LPS elevates cytokine levels in maternal fluids and fetal brain. Pro-inflammatory cytokines in maternal serum (4 h: control n = 7; LPS n = 7 and 24 h: control n = 6; LPS n = 6), amniotic fluid (4 h: control n = 28; LPS n = 26 and 24 h: control n = 24; LPS n = 20), and fetal brain (4 h control n = 19; LPS n = 25 and 24 h: control n = 11; LPS n = 10) at 4 and 24 h post maternal LPS (0.25 mg/kg) or saline administration on gestational day 15. Immunoaffinity electrophoresis analysis of fluid and tissue samples shows that cytokine protein levels are significantly elevated across the three maternal-fetal compartments at both time-points in offspring born to LPS-treated dams. Results are expressed as means ± SEM whereby * represents comparisons between LPS and control, p < 0.05 and # represents comparisons between LPS across time, p < 0.05 (2-way between subjects MANOVA).