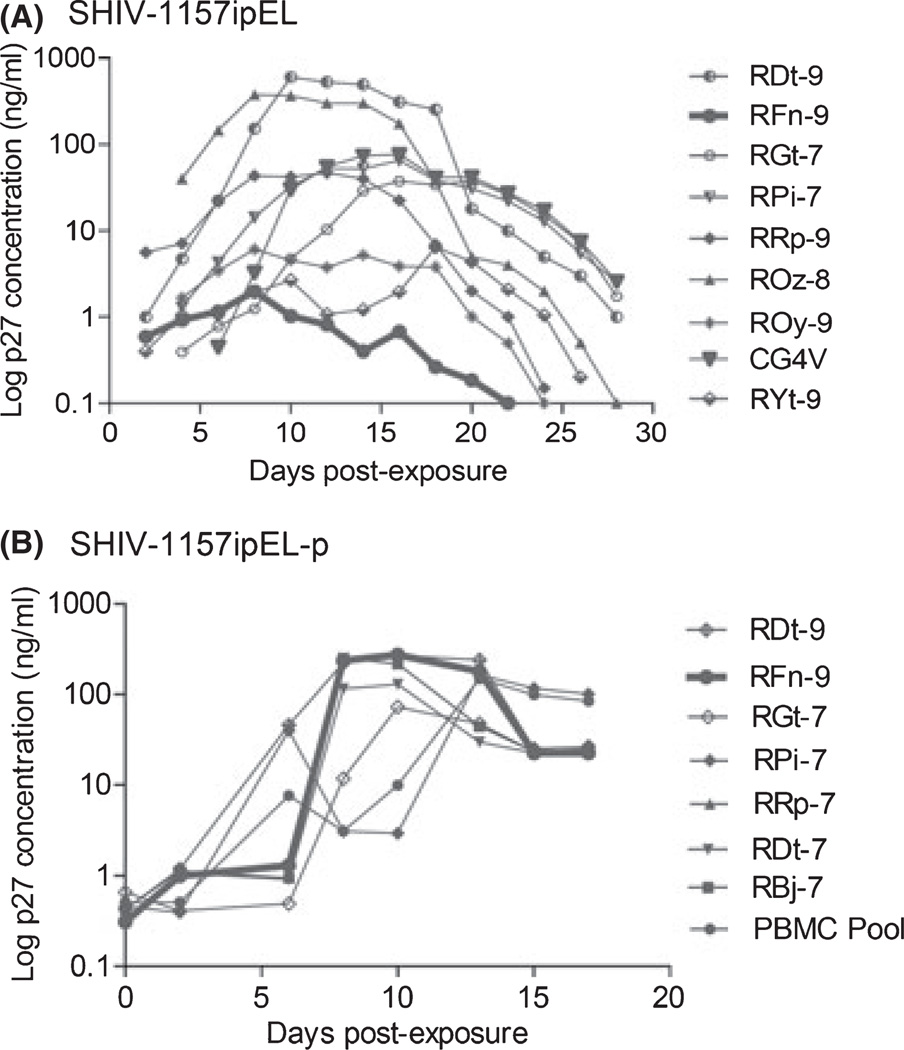
Fig. 1.
Replication of SHIV-1157ipEL and SHIV-1157ipEL-p in rhesus macaque (RM) PBMC. (A) PBMC from nine randomly selected naïve RM donors were stimulated with concanavalin A (ConA) and exposed to SHIV-1157ipEL-containing supernatant (Methods). The PBMC of RM RFn-9 did not support the replication of parental SHIV-1157ipEL (thick line). (B) PBMC from random donors were stimulated with Con A and exposed to passaged virus, SHIV-1157ipEL-p. Supernatants were harvested and p27 levels were measured at the time points indicated. Thick line, PBMC of RM RFn-9 (previously unable to support replication of parental virus, see under A) now yielded high levels of p27 production, indicating viral adaptation to the new host species. SHIV, simian–human immunodeficiency virus; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells.