Figure 1. The inhibitor PF-429242 blocks SKI-1/S1P-mediated processing of SREBP and ATF6, but not SKI-1/S1P autoprocessing.
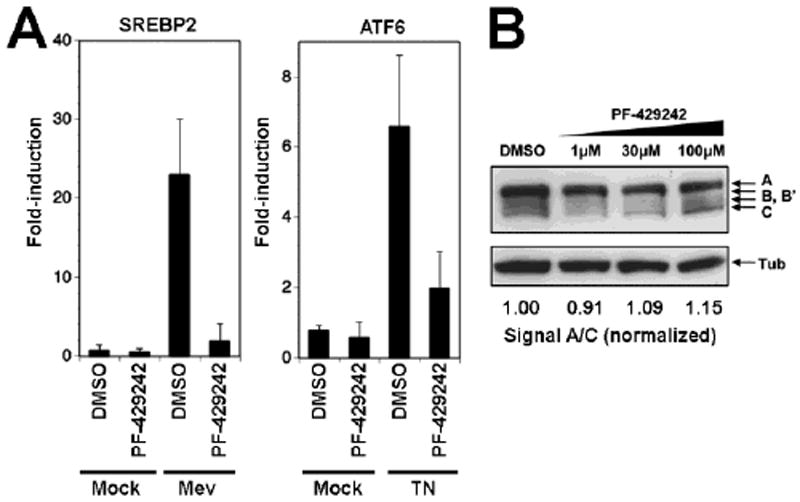
(A) Effect of PF-429242 on the ATF6-mediated induction of the heat shock 70kDa protein 5 (HSPA5) and the SREBP2-mediated upregulation of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A synthase (HMGCS1). CHOK1 cells were seeded in a 12-well plate and cultured overnight. To induce genes downstream of ATF6 cells were treated with 5 μg/ml tunicamycin (TN) for 4 hours. Genes downstream SREBP2 were induced by treating cells with 50 μM mevastatin (Mev) for 18 hrs. At 14 hrs after addition of mevastatin and at the same time with tunicamycin treatment, PF-429242 (10μM) or DMSO vehicle were added to the cells. At 4 hours post-treatment, cells were washed twice with PBS and total RNA isolated to perform RT-qPCR analyses as described in Materials and Methods. Data were normalized using the calibrator gene hydroxymethylbilane synthase (HMBS). Data are presented as fold-induction above levels for mock (DMSO)-treated cells (means ± SD; n = 3). (B) PF-429242 has no effect on SKI-1/S1P autoprocessing. SKI-1/S1P-deficient SRD12B cells were transfected with recombinant SKI-1/S1P containing a C-terminal V5-tag. Four hours post transfection, the indicated concentrations of PF-429242 were added and left throughout the experiment. After 48 hours, cells were lysed, total protein separated by SDS-PAGE and blotted to nitrocellulose. Blots were probed with an anti-V5 antibody using a HRP-conjugated secondary antibody and ECL for detection. The positions of full-length SKI-1/S1P (A), the form processed at the B/B’ site and the C site are indicated. Tubulin was included as a loading control. To assess the degree of autoprocessing, blots were subjected to densitometric analysis (Kunz et al., 2003b) and the signal of the band corresponding to the mature enzyme (C) normalized to the precursor (A).
