Figure 3. Inhibition of replication of LCMV variants by ribavirin (Rib).
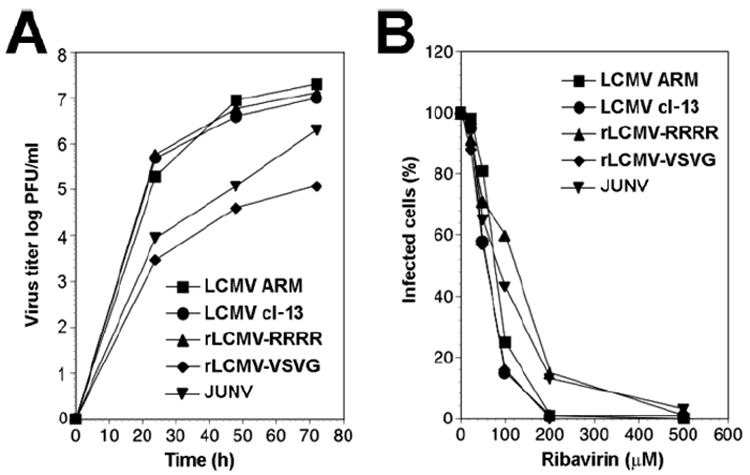
(A) Growth of LCMVs: A549 cells were infected with wild-type LCMV ARM53b, LCMV cl-13, rLCMV-RRRR, rLCMV-VSVG, and JUNV (MOI = 0.1) and virus titers determined in the supernatants after the indicated time points by plaque assay on VeroE6 cells. (B) Inhibition of replication of LCMV variants by Rib. A549 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate and cultured overnight, resulting in monolayers. Cells were infected with LCMV-ARM53b, LCMV cl-13, rLCMV-RRRR, rLCMV-VSVG, and JUNV at MOI=0.01. At 45 min post infection (p.i.), inoculums were removed and replaced by fresh medium containing increasing concentrations of Rib (25-500μM). At 48 hours p.i., cells were fixed and infection evaluated by IFA using mAb 113 to LCMV NP and mAb BG12 to JUNV NP. Cell nuclei were counterstained, 100 cells examined and NP positive cells scored. Each value is the mean of two independent experiments. Values were normalized against the controls (without drug).
